(Nano Telecommunication) Microstrip Antennas
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
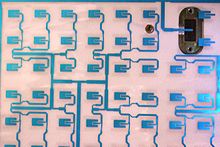
Note: Microstrip antennas are low profile antennas. A metal patch mounted on the ground with dielectric material between them forms a micro strip or patch antenna . In fact, there are antennas with very small size that have little radiation. Microstrip Antennas are popular for low-spec applications at frequencies above 100 MHz .
The Microstrip Antenna consists of a very thin metal strip that is held in place on a ground plate with a dielectric material. The radiant element and the power lines are placed on the dielectric material by the imaging process. A patch or micro-strip is usually selected as a square, circle or rectangle for ease of analysis and fabrication. Microstrip antennas are increasingly useful because they can be printed directly on the circuit board . Micro-strip antennas are low-cost, low-spec, and easy to build. The microstrip antenna is powered by a microstrip transmission line. The antenna, microtrip transmission line and ground plate are made of high conductivity metal (usually copper).
The microstrip antenna should be half the wavelength in the dielectric medium (substrate). The width of the micro-strip antenna controls the input impedance. Larger bandwidth can also increase bandwidth. For a square patch antenna powered by the above method, the input impedance will be about 300 ohms. By increasing the width, the impedance can be reduced. However, to reduce the input impedance to 50 ohms, you often need a very wide microstrip antenna that takes up a lot of valuable space. More width controls the radiation pattern. The bandwidth of the microstrip antenna is very small. Rectangular microstrip antennas are generally narrow. The bandwidth of rectangular microstrip antennas is usually 3%. Second, the microstrip antenna is designed to operate at 100 MHz, but has a resonance of about 96 MHz. This change is due to the marginal fields around the antenna, which makes the microstrip antenna appear longer. Communication between nano-devices is a major challenge related to the development of nano-antennas and related electromagnetic receivers. Reducing the size of a traditional antenna to hundreds of nanometers leads to very high operating frequencies . At THz band frequencies, the very large bandwidth available leads to the loss of a much higher path than the lower frequency bands.
Conclusion :
Microstrip antennas are low profile antennas. A metal patch mounted on the ground with dielectric material between them forms a micro strip or patch antenna . In fact, there are antennas with very small size that have little radiation. Microstrip Antennas are popular for low-spec applications at frequencies above 100 MHz .
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
PhD in Nano-Microelectronics