_ بخش (نانو و میکرو اِلکترومکانیکال MEMS)
اَفزاره های (نانو اِلکترومکانیکال MEMS) بخشی از گروهِ نانو سیستم الکترونیکی Nano System (شناخت از سر گروهِ این اصطلاح)
پژوهشگر و نویسنده: دکتر ( افشین رشید)
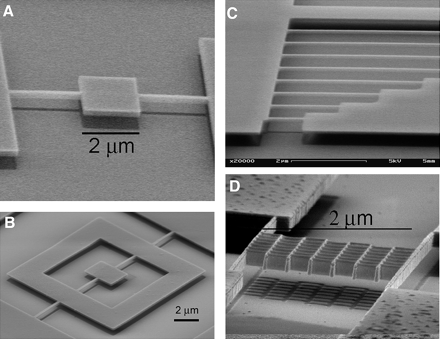
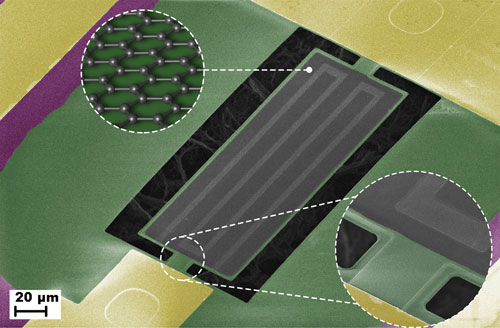
نکته : سیستم های نانو Nano System از مواد آلی یا معدنی مختلفی تشکیل شده اند که قابلیت و ویژگی های آنها مانند اندازه آنها از 1 تا 100 نانومتر هستند. ذرات نانو اجزای اصلی تشکیل دهنده سیستم های نانو Nano System و سیستم های (نانو و میکرو اِلکترومکانیکال MEMS) میباشند .
برای شناخت سیستم های (نانو و میکرو اِلکترومکانیکال MEMS) اولین توصیف گسترده نانو تکنولوژی به هدف خاص فناوری دستکاری دقیق اتم ها و مولکول ها برای ساخت محصولات در مقیاس کلان اشاره دارد که به عنوان نانو سیستم Nano System نیز شناخته می شود.
سیستم های (نانو و میکرو اِلکترومکانیکال MEMS) بخشی از نانو سیستم Nano System وعملکردی در مقیاس مولکولی است. این کار هم کارهای فعلی و هم مفاهیم پیشرفته تر را در بر می گیرد. به معنای اصلی آن ، فناوری نانو به توانایی پیش بینی شده برای ساخت اقلام از پایین به بالا ، با استفاده از تکنیک ها و ابزارهایی گفته می شود که برای ساخت محصولات کامل و با کارایی بالا تولید می شوند.نانو سیستم Nano System ایده "مونتاژ" در مقیاس نانو را ارائه داد که می تواند کپی خود و خود را بسازد. از دیگر موارد پیچیدگی دلخواه سیستم های (نانو و میکرو اِلکترومکانیکال MEMS) با کنترل اتمی در نانو سیستم Nano System ها بسیار گسترده و کاربردی میباشد. نانو کامپیوتر و نانو اسمبلر ها نیز زیر گروه نانو سیستم ها Nano System میباشند. نانو ذرات اجزای اصلی تشکیل دهنده تمام نانو سیستم ها Nano system میباشند.در شناخت سیستم های (نانو و میکرو اِلکترومکانیکال MEMS) میتوان گفت : برای تولید ذرات نانو با کمک فناوری نانو می توان در اتمها از طریق کنترل خصوصیات تغییراتی ایجاد کرد. زمانی که مواد در مقیاس نانو مطالعه و بررسی می شوند واکنش های و رفتار اتمها در مقایسه با حالتی که مطالعه در سطح مولکولی انجام می شوند کاملا متفاوت است چرا که در این قلمرو خصوصیات فیزیکی مواد تغییر می کند این درست مانند این است که در توپی را در محفظه ای بیندازید و توپی دیگری را از آن محفظه بیرون آورید. تفاوت در قلمرو نانو به اندازه ای است که حتی رنگ، نقطه ذوب، خصوصیات شیمیایی و غیره مواد در خارج از این محدوده کاملا متفاوت است.
نتیجه گیری :
سیستم های نانو Nano System از مواد آلی یا معدنی مختلفی تشکیل شده اند که قابلیت و ویژگی های آنها مانند اندازه آنها از 1 تا 100 نانومتر هستند. ذرات نانو اجزای اصلی تشکیل دهنده سیستم های نانو Nano System و سیستم های (نانو و میکرو اِلکترومکانیکال MEMS) میباشند .
پژوهشگر و نویسنده: دکتر ( افشین رشید)
دکترایِ تخصصی نانو _ میکرو الکترونیک