_ Nanoplasmonics and Nanoelectronics Model Section
Investigation of nanoplasmonics and the interaction process between electromagnetic waves and conduction electrons in nano-sized metals
_i59w.gif)
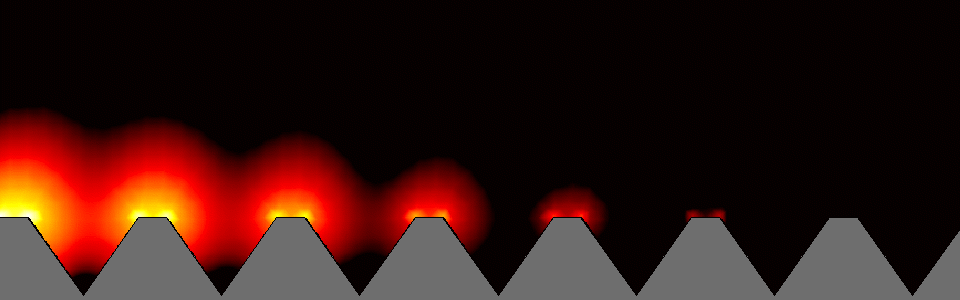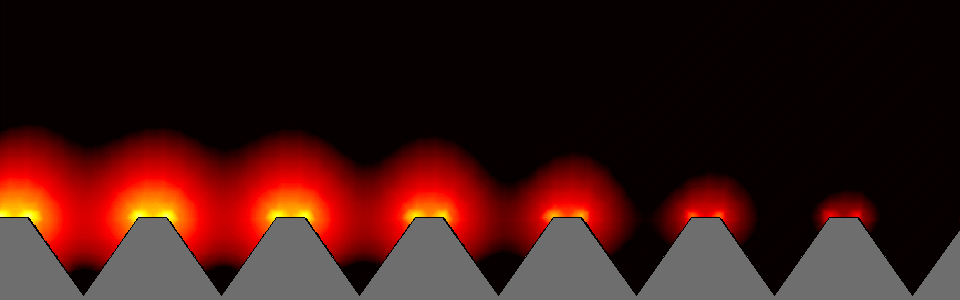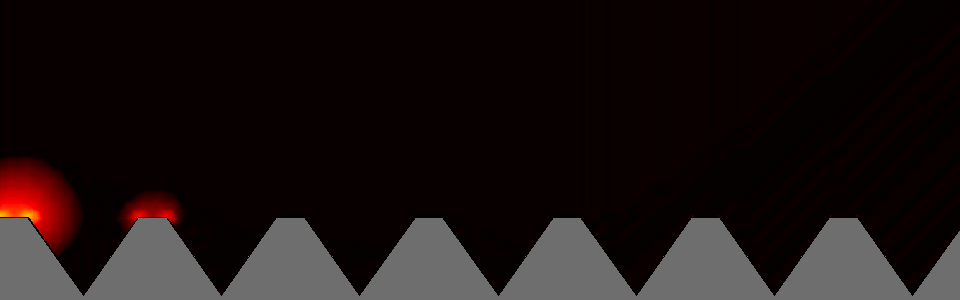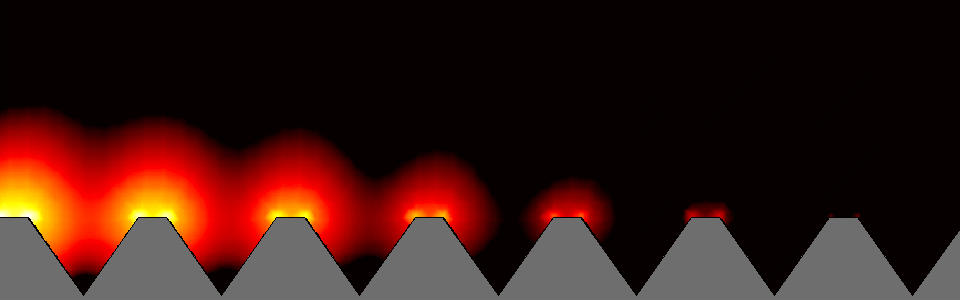
In the structure that constitutes nanostructures (nanoplasmonics), the created volume of the electromagnetic field is locally compressed and enhanced. Small changes in the dielectric around the nanovolume affect the resonance of surface plasmons, so that these changes are manifested in the amount of scattered radiation, absorbed radiation or change in its wavelength. Nanostructure is defined as any structure with one or more dimensions and is measured in the nanometer scale range. Nanostructures refer to materials or structures that have at least one dimension between 1 and 100 nanometers . The importance of the nanoscale is in changing the properties and characteristics of materials at these dimensions. Properties such as electrical conductivity, electromagnetic properties, etc. The beginning of changing the properties of materials by miniaturization depends more than anything on the type of material and the desired property. For example, as the dimensions of a material are reduced , generally some of the electromagnetic properties of nanomolecular materials such as the conductivity of nano particles in materials improve. This increase in strength does not only occur in the range of a few nanometers, and the strength of a material of a few tens or even hundreds of nanometers may be much greater than that of a large-scale bulk material. These changes can be measured using optical properties. The oscillation of surface electrons and the electric field around them shows the resonance of localized surface plasmons.
For example, as the dimensions of a nanostructured material (nanoplasmonics) decrease , some of the mechanical properties of the material, such as strength, generally improve. This increase in strength does not occur only in the range of a few nanometers, and the strength of a material of several tens or even hundreds of nanometers may be much greater than that of a large-scale bulk material. On the other hand, changes in some properties, such as color and magnetic properties, may occur in dimensions of only a few nanometers. Nanoplasmonics is expressed based on the interaction process between electromagnetic waves and conduction electrons in metals with nanoscale dimensions . Analytically, the reason for the rapid drop in energy of electrons passing through metals is that this energy is spent on the collective and oscillatory motion of free electrons in the metal, which is called a plasmon. These nanostructures consist of metal and dielectric, whose dimensions are below the excitation wavelength (the wavelength of the radiation that excites plasmonic waves).
Conclusion:
Nanoelectronics/ plasmonics is based on the interaction process between electromagnetic waves and conduction electrons in metals at nanoscale. Analytically, the reason is the rapid energy loss of electrons as they pass through metals, and it was concluded that this energy is spent on the collective and oscillatory motion of free electrons in the metal, which he called plasmons.
Researcher and Author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized PhD in Nano-Microelectronics