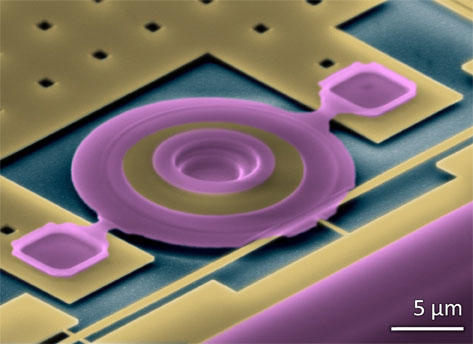
Department of systems (nano and microelectric and mechanical MEMS )
Step 5 (Polysilicon Deposit)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
 Note: To make and prepare systems (nano and microelectric and mechanical MEMS ) (a thin film of polysilicon is deposited on silicon dioxide. For example, polysilicon can be used in the LPCVD system at 600 degrees centigrade in a confined space of silane (SiH4) to settle.
Note: To make and prepare systems (nano and microelectric and mechanical MEMS ) (a thin film of polysilicon is deposited on silicon dioxide. For example, polysilicon can be used in the LPCVD system at 600 degrees centigrade in a confined space of silane (SiH4) to settle.
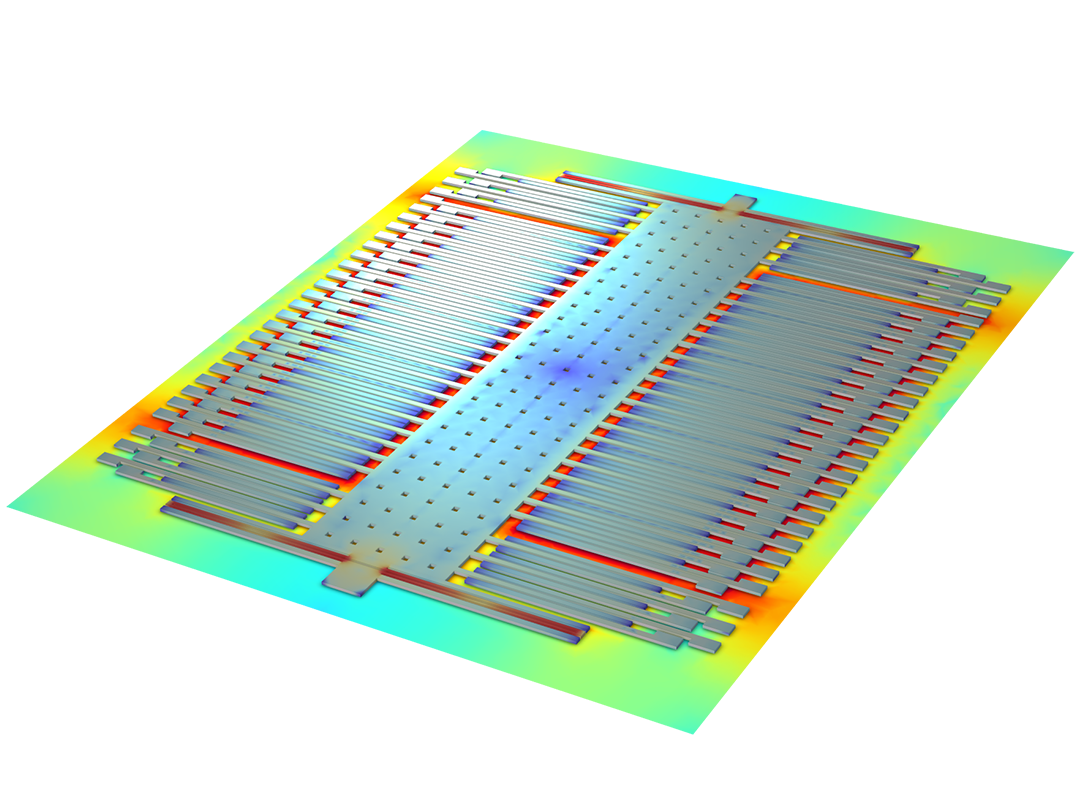
In the process of making and preparing systems (nano, microelectric and mechanical MEMS ) , the deposition speed in normal conditions is 65 to 80 angstroms per minute (Almin), which minimizes the internal pressure and prevents bending and folding . The thin polysilicon must be stress-free or have a tensile internal stress.Thickness of the thin film is more than ((4)) microns.
As in step 5 (deposition of polysilicon deposits ) for the construction of and mechanical MEMS)systems, the average diameters of carbon nanofibers provided are from 125 to 150 nanometers, depending on their grade and length, from 50 to 100 micrometers. These nanofibers are much smaller in diameter than continuous or milled carbon fibers (5-10 nm) and significantly larger than carbon nanotubes (1-20 nm), yet offer many of the same advantages. Carbon nanofibers are refined after production in order to transfer different properties on the surface. In general, there are three types of nanofibers available in the manufacturing and supply of (nano, microelectric and mechanical MEMS ) systems . simple pyrotically to remove surface hydrocarbons and produce a pristine surface for chemical bonding. This type of nanofiber also serves as a precursor to the other two lists. To provide the best combination of mechanical and electrical properties, it is thermally placed at a temperature of 1500 degrees Celsius, while to produce a product without a catalyst and to maximize the thermal conductivity properties in composites, it reaches a temperature of 2900 degrees Celsius. Carbon nanofibers (CNF) are discontinuous, highly graphitic, highly compatible with most polymer processing techniques, and can be dispersed isotropically or anisotropically. CNFs have excellent mechanical properties, high electrical conductivity, and high thermal conductivity that can be transferred to a wide variety of matrices including thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, ceramics, and metals . 5 (Polysilicon Deposit ) is for the construction of (nano, micro, electrical and mechanical MEMS ) systems . Carbon nanofibers also have a unique surface area, which facilitates functionalization and other surface modification techniques to tailor and engineer the nanofibers to the host polymer or its application.
In step 5 (deposition of polysilicon deposits) for the construction of (nano and microelectrical and mechanical MEMS ) systems, nanopolymers, unlike most composites, cannot be separated in solutions and include amino groups as the main ingredients of the formation It is a donor that may consist of all combinations of carbon, oxygen and nitrogen atoms, depending on the chemical nature of the monomers used in polymer synthesis. A polymer or copolymer containing dispersed nanoparticles is a nano polymer. These nanopolymers can be linear or branched. Linear nanopolymers or polymalic acid have functional groups distributed along the entire length of the polymer, while branched polymers such as dendrimers usually carry them at the molecular level. Nanofiber _ It is a term that refers to fibers with a diameter of less than 500 nm. When the diameter of polymer fibers is reduced from microns to several hundreds of nanometers, they can obtain amazing properties such as very high surface-to-volume ratio, suitable flexibility, and high mechanical efficiency for the construction of (nano- and micro-electrical and mechanical MEMS ) systems . . The main property of fibers is a very high ratio of length to diameter. Micron fibers are fibers in which the filaments are less than one denier in mass per unit gram per 9000 meters, less than one micrometer are called nanofibers . These fibers with relatively short lengths of a few microns and with a diameter of less than 500 nanometers, such as (nano- and micro-electrical and mechanical MEMS ) systems They are one-dimensional structures. In general, there are several methods for producing nanofibers, some of which include stretching method, separation of multicomponent fibers, mold method, blowing, phase separation, self-assembly of macromolecules, electrolysis , etc. Resena is the production of polymer fibers with a diameter below nanometers.
Conclusion :
To make and prepare (nano- and micro-electrical and mechanical MEMS ) systems, a thin film of polysilicon is deposited on silicon dioxide . For example, polysilicon can be produced in the LPCVD system at 600 degrees Celsius in a confined space of silane (SiH4 ) to be settled.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics