Section "Nanospin Electrons" - Nanoelectronics
Self-assembly kinetics in self-assembled biomolecular “nano-spin electrons” ( over 1 to 10 μm in more than 75% of cases)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
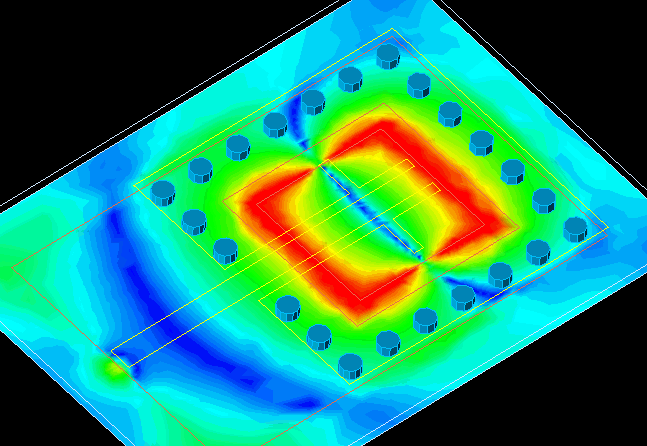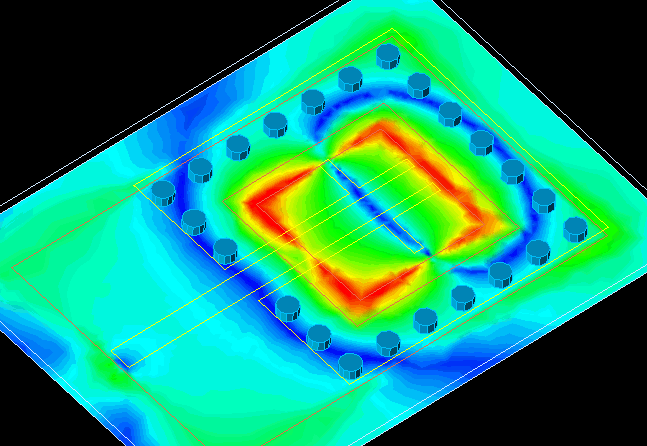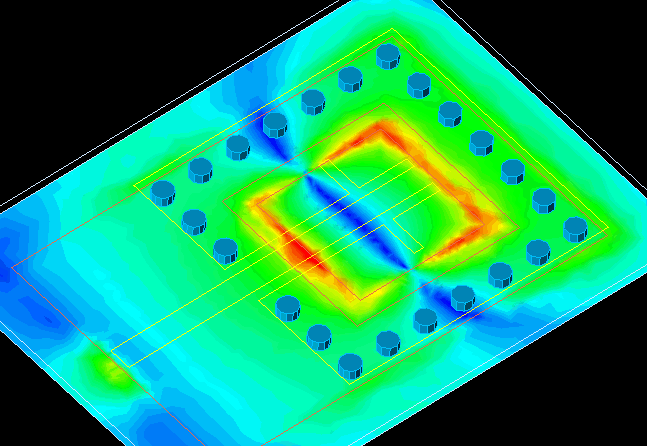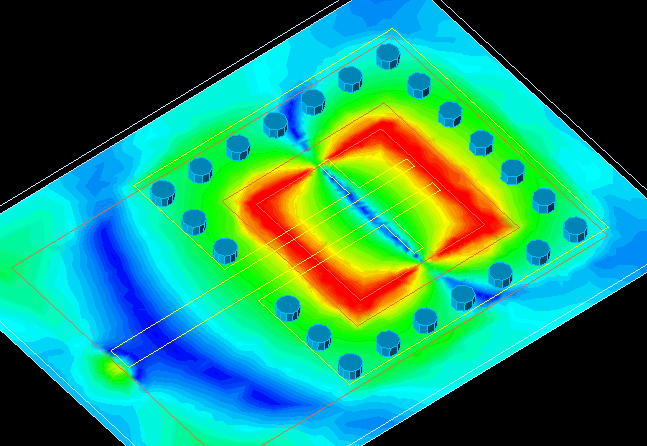
Note: Within the particle structure of nanobiosensors, "nano-spin electrons" are usually organized using local assembly rules that order; They produce with a long range . Because these rules can take into account the structure and current state of the cell, they can assemble complexes, organelles, or skeletal structures around existing cellular components to form integrated architectures.
Although many methods have been developed to make self-assembled biomolecular "nano-spin electrons" .A few can be designed to assemble structures whose shape depends on the identity and organization of structures already present in the environment. " Nanospin electrons" can be grown to bind pairs of molecular markers with different separation distances and relative orientations. "Electron nanospins" form at these hotspots and grow as their free ends dissipate. Nanospin electrons can then join to form stable, end-to-end connections, and unbonded nanospins can selectively melt. Junctions between labeled pairs are separated by more than 1–10 μm in more than 75% of cases and can form one surface or three dimensions. This point-by-point assembly process demonstrates how the kinetics of self-assembly can be tailored to produce structures with desired properties rather than a specific shape.
Analyzer, sensor, converter and detector are the components of the nano sensor system and its feedback reaches the nano sensor from the detector. Sensitivity, specificity and ease of implementation are the main goals in the design of a nanosensor. Nanosensors typically work by monitoring electrical changes in the sensing material. For example, nano-sensors based on "nano-spin electrons" work in this way. When a molecule of nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) is present, it removes an electron from the nanotube, which in turn causes "Nano spin electrons" have less conductivity. If ammonia (NO 3 ) is present, it reacts with water vapor and gives an electron to "nano spin electrons". donates, and conducts it. By reacting "nano spin electrons" with different coating materials, they can be made sensitive to certain molecules and immune to others. Like chemical nanosensors, mechanical nanosensors also tend to measure electrical changes.
Conclusion :
Within the particle structure of nanobiosensors, "nano-spin electrons" are usually organized using local assembly rules that order; They produce with a long range . Because these rules can take into account the structure and current state of the cell, they can assemble complexes, organelles, or skeletal structures around existing cellular components to form integrated architectures.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics