Interaction of Electronic Particles in Nano Memory Moulcolar (PhD Nano _ Microelectronics)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
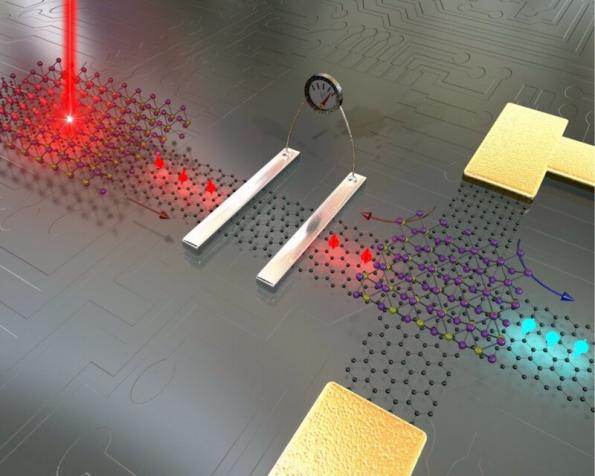
Note: The interaction of absorbed nano-graphene particles causes this change in electrical conductivity at the level of Nano Memory Moulcolar . Absorption of small amounts of nano-electrons with very low molecular motion alters the resistance of nano-graphene , which is commensurate with the molecular nanoparticles of graphene Nano Memory Moulcolar .
Common nanoelectronic technologies in nano-memories hardly meet the demands, but nanotechnology offers better solutions. One of the new data storage tools is the use of nickel quantum dots in nanometer sizes that are expected to be used to store terabytes of data, even at home and in personal use. Given the relatively large (physically) storage devices we currently have, and the fact that we need sizes around GIGABYTE in various fields, there is a great potential for activity in this area.Each quantum dot contains a separate ball of several hundred atoms that can have one of two magnetic states. This allows them to contain a bit of information (zero or one), as is customary in machine computing. On common hard disks, the data bits must be spaced far enough apart to avoid retaliation. Quantum dots act as completely independent units that are not structurally interconnected, so they can be somewhat closer together. They can be arranged to a certain density that allows any type of information up to 5 terabytes to be stored in a space the size of a postage stamp. Activities should continue until these nanoparticles work better and work with other computing devices such as silicon chips.
Conclusion :
The interaction of absorbed nano-graphene particles , which changes the electrical conductivity at the surface of Nano Memory Moulcolar Graphene . Absorption of small amounts of nanoelectrons with very low molecular motion alters the resistance of nano-graphene , which is commensurate with the molecular nanoparticles of Nano Memory Moulcolar .
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
PhD in Nano-Microelectronics