Explanation of Buckminsterfullerene from the perspective of nanoscience and nanoelectronics (PhD in nano-microelectronics)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
In nanoscience and nanoelectronics, carbon nanotubes have many applications. Carbon is one of nature's most amazing elements, found in nature in four different forms: graphite, diamond, nanotubes, and buckwheat. All four of these shapes are solid, and in their structure the carbon atoms are arranged side by side in a complete and orderly manner.
Carbon is one of the most important elements in nature and its many applications in human life, well confirms this point. Steel, for example, which is one of the main engineering alloys, is obtained by dissolving about two percent of carbon in iron; By changing the percentage of carbon to only a few hundred percent, all types of steel can be obtained. "Organic chemistry" is also a science that studies compounds containing "carbon" and "hydrogen", and polymer engineering is based solely on the element carbon. Carbon is found in four different forms in nature , all of which are solid forms, and in their structure carbon atoms are arranged next to each other in a completely regular manner.
These structures are:
01.Graphite
02.الماس
03. (Bucky wings) Like C60
04 .Panules
Graphite is one of the most important carbon structures in nature and is formed by placing six carbon atoms next to each other. These carbon atoms are combined to form a regular hexagon, and from their sum, a plate is formed that is considered as a (graphite layer).
Carbon atoms are bonded together by covalent bonds, which are strong bonds. It should be noted that the carbon atoms used in a graphite layer cannot be covalently bonded to carbon outside this layer. Therefore, a graphite layer is attached to the lower layer through van der Waals bonds, which are weak bonds. This causes the graphite sheets to slide easily on top of each other. For this reason, this combination is used in "lubrication" and "lubrication". This is also the reason for the softness of the surfaces written on them with a pencil .
Diamonds 1-2
At very high temperatures and pressures, carbon is stable as a diamond in which each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four atoms. Due to the presence of strong covalent carbon-carbon bond among the hardest natural materials with hardness of 01 on a scale of Morse's. The same structure has created amazing properties in diamonds, including the thermal conductivity of several times that of copper and the melting point of about 3111.
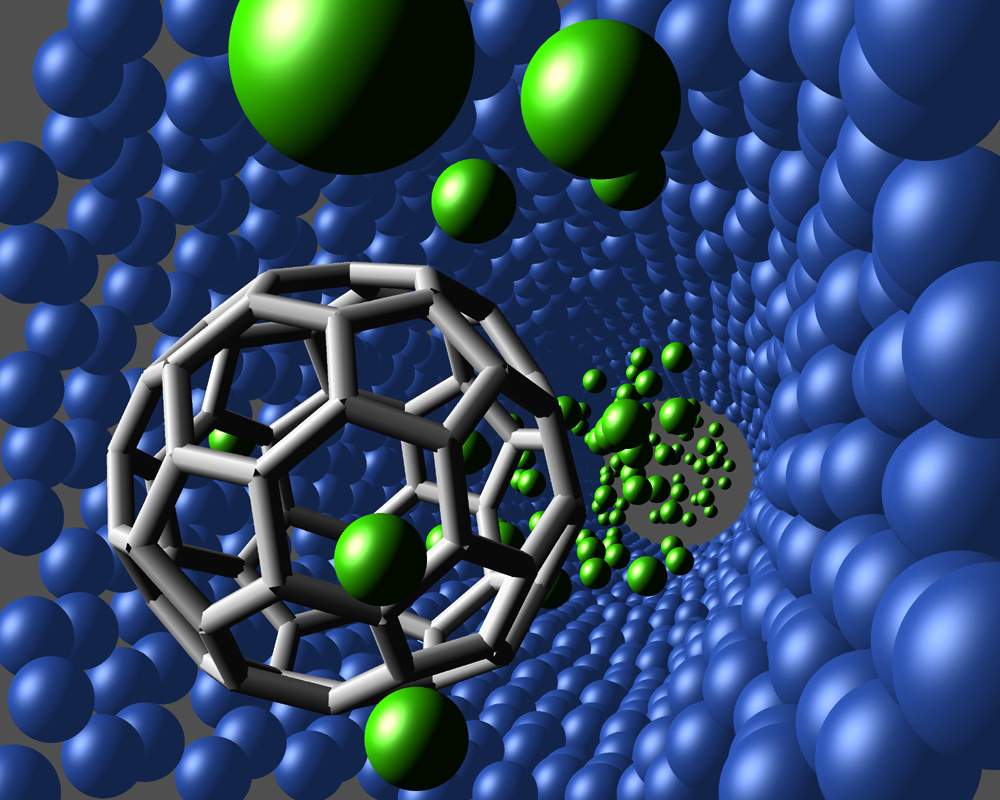
3-1 - Bucky wings
Buckles are hollow, ball-shaped carbon structures, the most famous of which is C60 or fullerene. The C60 has a structure similar to a soccer ball . The carbon atoms in it are connected by a covalent bond in the form of pentagons and hexagons. In fact, this sphere is composed of 30 parts, 01 of which are hexagonal and 00 of which are pentagonal. Bucky wings have many uses due to their chemical properties and hollow and cage-like shape. Bucky wings are extremely stable and can withstand very high pressures and temperatures. Buckwheat carbon atoms can react with atoms and molecules without altering their stability or spherical structure.
4-1 -Carbon nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes are one of the most important and widely used carbon structures recently discovered. They have unique properties and characteristics . Carbon nanotubes, in addition to being very strong, also have good flexibility and flexibility. One of their applications is composite. The most important property of nanotubes is their electrical conductivity, which varies depending on the order of the atoms .
Conclusion :
Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical molecules with open or closed ends. The structure of nanotubes is like a sheet of rolled graphite. To better understand the structure of a graphite nanotube, consider. Locate the atoms in a row with (m, n), which represents the coordinates of a point on the plane. So that the coordinates n correspond to the column of atoms and the coordinates m correspond to the row of atoms. As we know, to make a pipe from one plate, it is enough to put one point of the plate on another. A nanotube is like a graphite plate that is shaped like a tube. Depending on how the two ends of the graphite plate are connected, we will have different types of nanotubes.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
PhD in Nano-Microelectronics