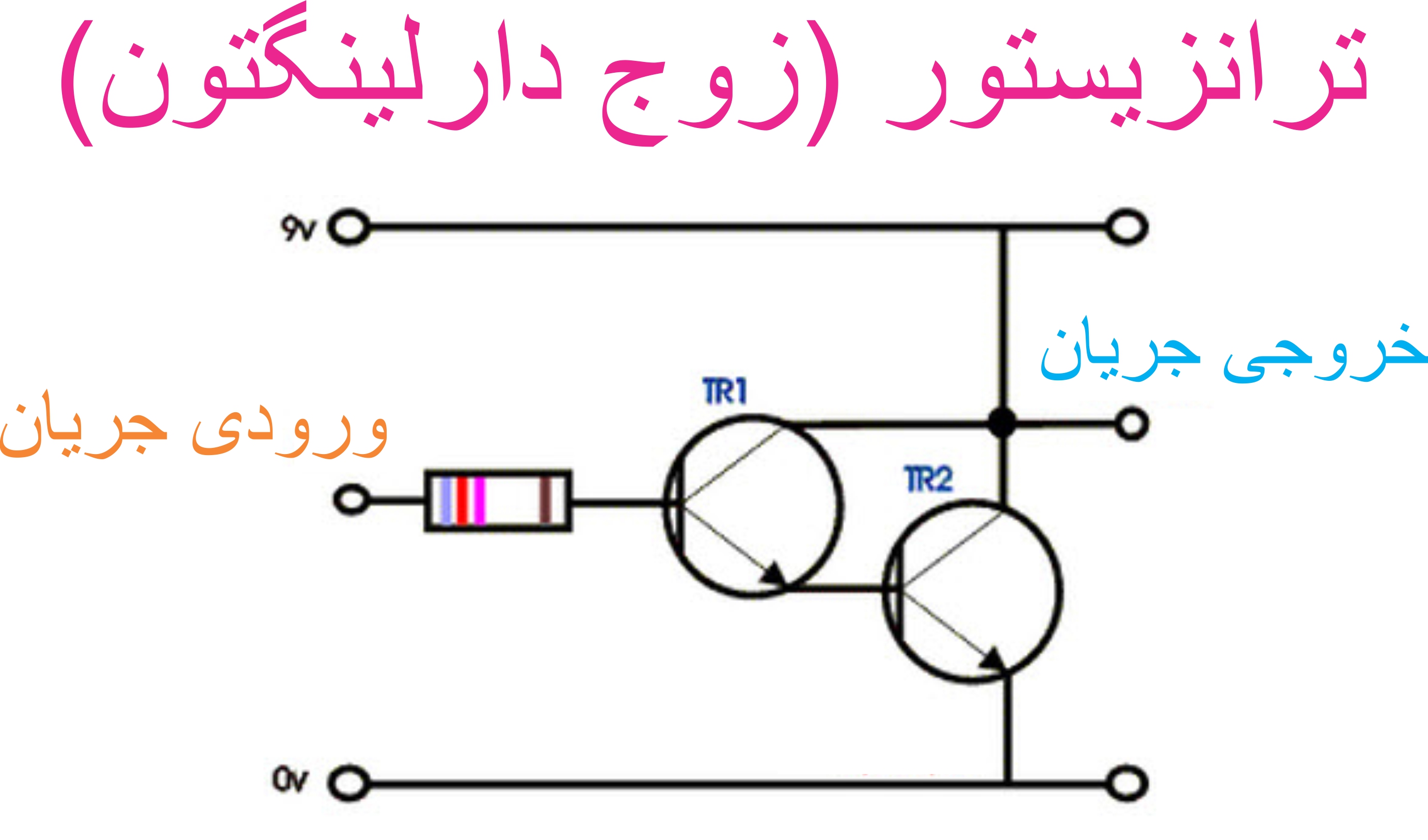
Section _ Understanding (Darlington transistor ) or Darlington pair
Function and role (a sensitive transistor in current amplification applications) Darlington transistor = pair or pair
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
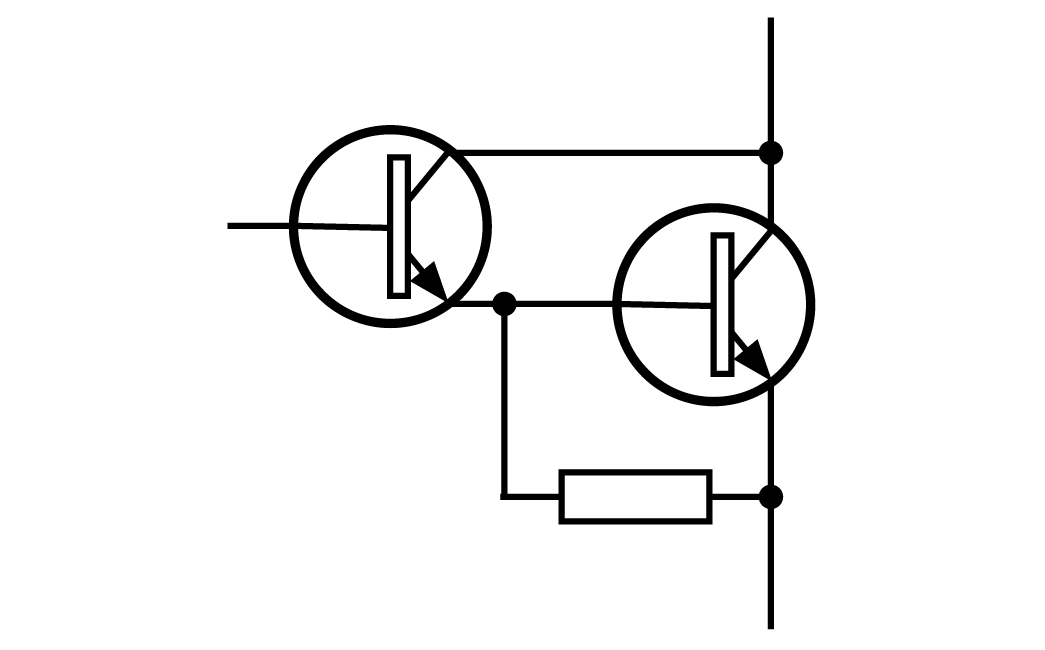
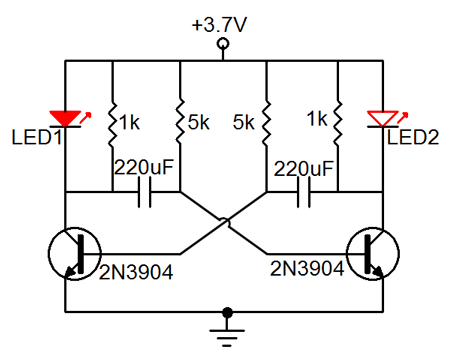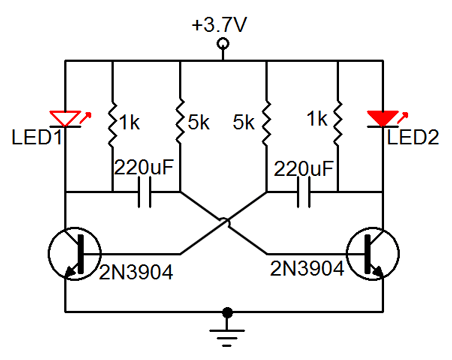
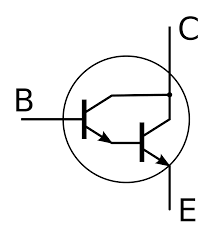
Note: A Darlington transistor is a special arrangement of two standard NPN or PNP bipolar junction transistors (BJT) connected together. The emitter of one transistor is connected to the base of the other to produce a more sensitive transistor that can handle much higher current, useful in applications where current amplification or switching is required.
A Darlington transistor pair can be made from two separate bipolar transistors connected together or a single device manufactured commercially in a single package with standard: base, emitter and collector connectors and is available in a variety of styles and voltage (and current) ratings. In both NPN and PNP versions, the Darlington transistor is used as an amplifier. TheDarlington transistor configuration and structure of the two bipolar transistors increases the switching current for a given base current.
These types of transistors do not work well at voltages below 3 volts, but for voltages above 3 volts, they turn on completely and go into saturation with very little current. These transistors are often used for switching (turning on and off).
_uay6.gif)
Power: Power Darlington transistors are usually used to connect a large consumer such as a motor to a microcontroller or a weak output with an hfe of at least 750 with a continuous current tolerance of 8 amps (you must take care to keep the transistor cool. At a minimum, use a heat sink and silicone paste or paper).
Darlington transistor operation:
A Darlington pair behaves like a single transistor with a high current gain (approximately the product of the gains of the two transistors).
Darlington pair as a transistor:
The Darlington pair can be used as a large β transistor in emitter follower circuits. Darlington pairs with β of about 30000 are commercially available on integrated circuits. An example of such a transistor is the MJ1000. The MJ1000 is a power Darlington transistor with β of about 1000, capable of delivering 10 A, and a collector-emitter voltage of up to 80 V.

Application of Darlington transistor
In many electronic applications, control circuits only need to switch a DC voltage or current on and off directly, because the components connected to their outputs, such as LEDs and displays, require a few milliamperes of DC power to operate at low DC voltages, so they can be driven directly by the output of standard logic gates. Sometimes we need more power to drive an output, such as when we want to drive a DC motor, which can be powered by a regular logic gate or microcontroller. If the logic components cannot provide the required current, we will need additional circuitry to drive the desired output.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized PhD in Nano-Microelectronics