_ Department of Integrated Circuits (ASIC)
( RLT and TRL logic ) in the circuit structure (ASIC complex)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
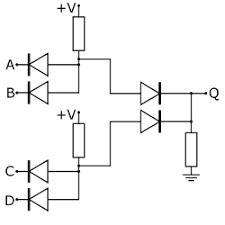
Note: In the structure of ASIC integrated circuits , Resistor-Transistor Logic or RTL is an outdated technology for designing and manufacturing digital circuits that do not use logic gates consisting of anything other than transistors and resistors . RTL gates are now rarely used in modern digital electronics design, as they have several drawbacks such as bulkiness, slow speed, reduced cooling, and poor noise margins. A basic understanding of RTL is useful for anyone who wants to learn about TTL, which has been widely used in digital devices such as logic gates, latches, buffers, counters, and more for years.
ASIC integrated circuits are known as direct connection transistor logic gates . An RTL gate is a gate where the bases of the transistors are connected directly to the inputs without any base resistance. Therefore, if all the base resistors are removed, the RTL NOR gate becomes a TRL NOR gate. Without base resistors, TRL gates are more cost-effective and simpler to build than RTL gate circuits with base resistors. The main drawback of RTL gates is that they suffer from a phenomenon known as current jamming . Ideally, several transistors connected in parallel will divide the load current equally when all are in saturation. However, in the real world, the saturation points of different transistors are achieved with different levels of input voltage to the bases. Likewise, transistors that are in parallel and have the same input voltage (which is common in TRL circuits) do not divide the load current equally between them.
In an RTL circuit, the collector output of the driver transistor is connected directly to the base resistor of the driven transistor. Circuit analysis easily shows that in such an arrangement, the differences between the gate structures are not so great. For this reason, it is known that RTL gates have a weak noise margin compared to DTL and TTL gates .
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics