_ Nanoelectronics and Plasmonic Particles Department
Nanoelectronics and Localized Surface Plasmons
Researcher and Author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Note: In nanoelectronics, surface plasmon excitation is the coherent and cumulative oscillations of metal electrons excited by radiation.
The oscillation condition is that the frequency of the emitted photons is the same as the natural frequency of the surface electrons (which is to overcome the core-core force). Surface plasmon resonance in nanometer-sized structures is called localized surface plasmon resonance.
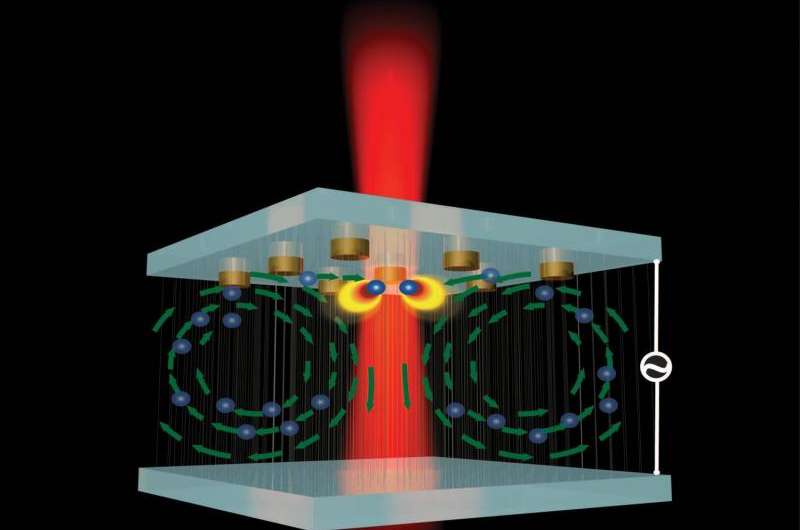
Localized surface plasmons are the non-diffusive excitation of conduction band electrons in metallic nanostructures to which an electromagnetic field is coupled. Plasmonic waves are generated by the scattering problem from a conducting nanoparticle whose dimensions are below the wavelength of the excitation electromagnetic field. These nanostructures consist of a metal and a dielectric whose dimensions are below the excitation wavelength (the wavelength of the radiation that excites the plasmonic waves). Plasmonics is based on the interaction process between electromagnetic waves and conduction electrons in metals with nanoscale dimensions. Analytically, the reason for the rapid energy loss of electrons when passing through metals is that this energy is spent on the collective and oscillatory motion of free electrons in the metal and is called a plasmon.
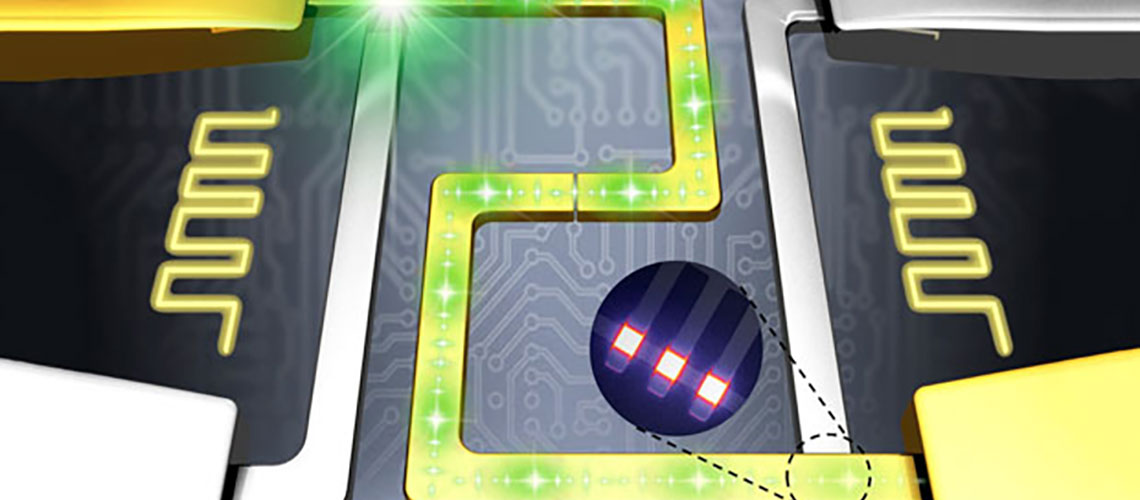
One-dimensional localized surface plasmon nanostructures can be used for electronic connections, while zero-dimensional and two-dimensional nanomaterials do not. The main basis of nanotechnology is the use of materials. Every material in space has three dimensions of length, width, and height. With the technological approach towards the accumulation of optoelectronic circuits, the problems of manufacturing and phenomena that helped prevent further compression of the structure, led to the study and use of plasmonic structures and plasmonic waves. These nanostructures consist of metal and dielectric whose dimensions are below the excitation wavelength (the wavelength of the radiation that excites the plasmonic waves).