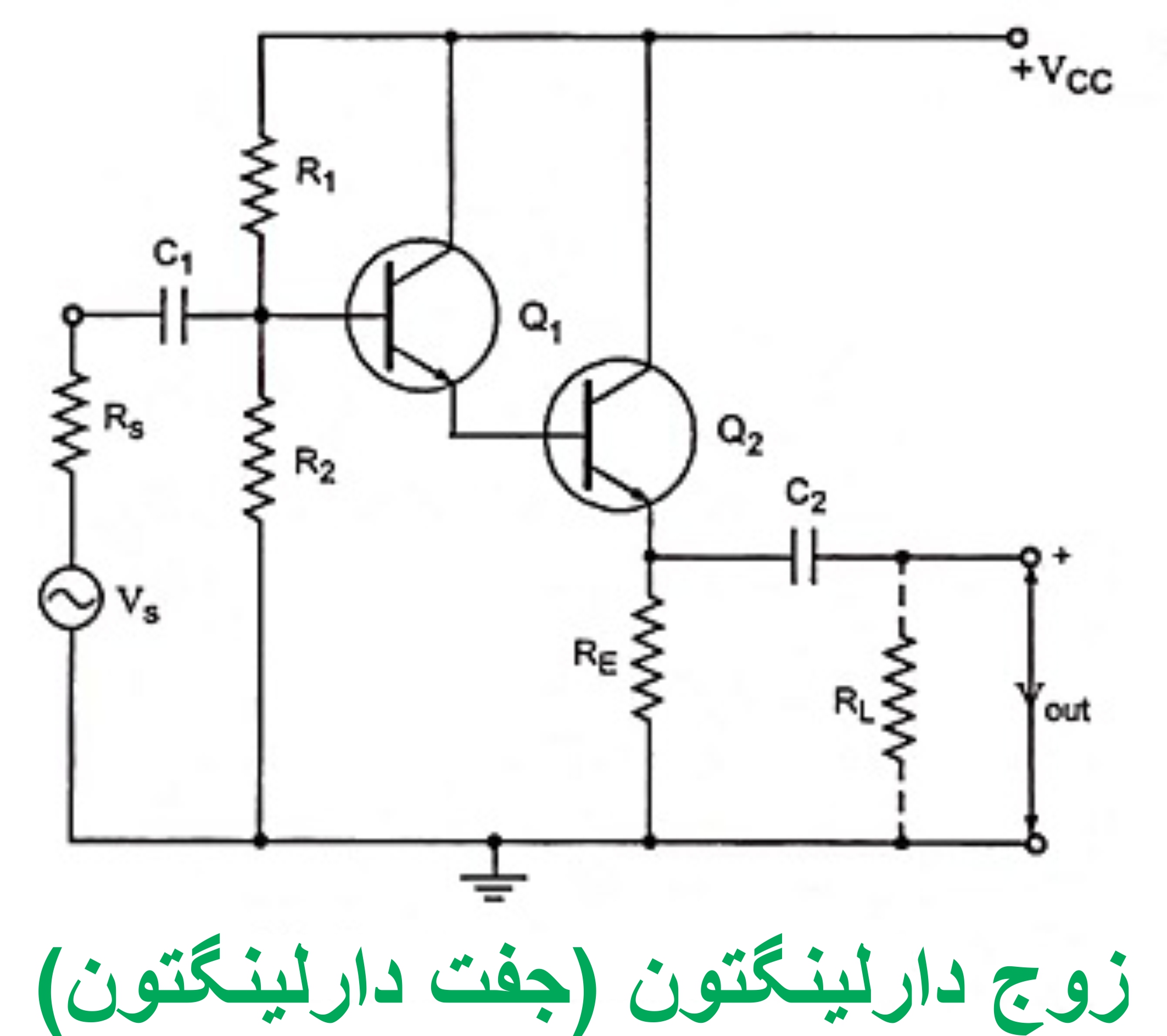
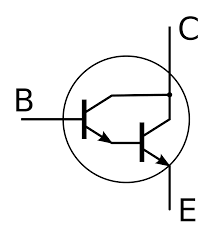
Section _ Understanding (Darlington transistor ) or Darlington pair
THT Darlington transistors ( Darlington pairs) do not perform well below (3 volts).
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Note: A Darlington transistor is a special arrangement of two standard NPN or PNP bipolar junction transistors (BJT) connected together. The emitter of one transistor is connected to the base of the other to produce a more sensitive transistor that can handle much higher current, useful in applications where current amplification or switching is required.
A Darlington transistor pair can be made from two separate bipolar transistors connected together or a single device manufactured commercially in a single package with standard: base, emitter, and collector connectors and is available in a variety of styles and voltage (and current) ratings in both NPN and PNP versions . The Darlington transistor is used as an amplifier.
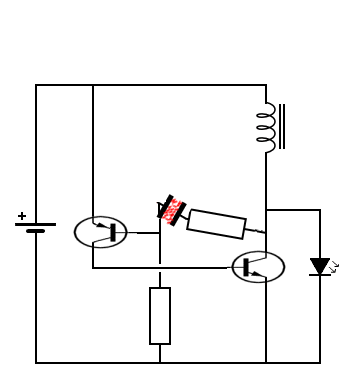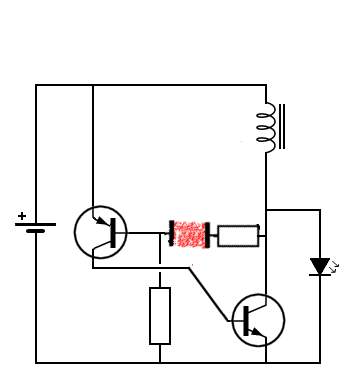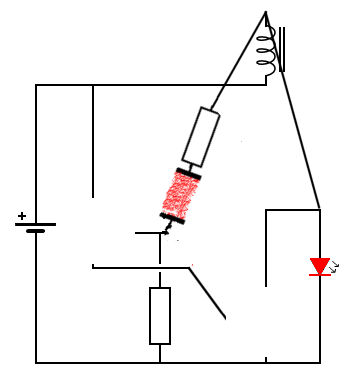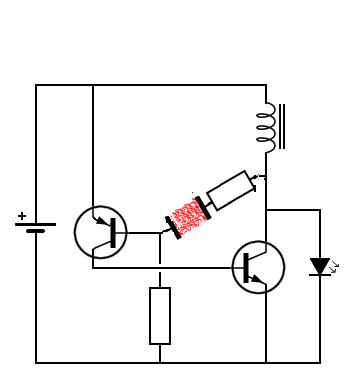
The Darlington transistor configuration and structure of two bipolar transistors increases the switching current for a given base current. These types of transistors do not work well at voltages below 3 volts, but for voltages above 3 volts they turn on completely and go into saturation with very little current. These transistors are often used for switching (turning on and off).
How to test with a multimeter
In all transistors, the base terminal allows current to pass through to both other terminals. We put the ohmmeter in diode test mode. Place the positive end of the ohmmeter on one of the transistor terminals and place the positive end on the other two terminals respectively. If the terminal on which the positive end of the ohmmeter is located allows current to pass through to both other terminals, it is the base terminal. The base terminal does not allow current to pass through to both collector and emitter terminals equally. After the base terminal is determined, the base terminal allows current to pass through to whichever terminal it allows more is the collector terminal and the other terminal is the emitter ( base-collector resistance is less than the base-emitter resistance). The terminals of a healthy transistor allow current to pass through to each other only from one side. For example, if the positive end of the ohmmeter was on the base and the negative end of the ohmmeter was on the emitter and the two terminals were allowed to pass through, by moving the two ends of the ohmmeter, the two terminals should not allow current to pass through to each other. No two terminals of the transistor should be short-circuited.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized PhD in Nano-Microelectronics