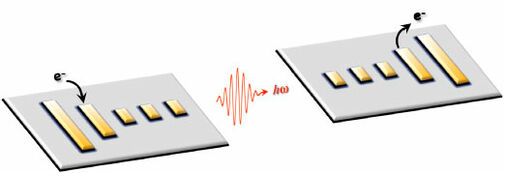
Communication-electrical nano antennas) The efficiency of a classic nanotube antenna is about -90dB
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Note: The efficiency of a classical nanotube antenna is around -90dB, which is due to resistive losses.
Meanwhile, the dimensions of the antenna and nano system or nano sensor set, operating frequency, power losses, the scope and dimensions of the sensor network, the structure and facilities of the feeding system and the physical communication platform between different parts of a nano system, major factors and parameters are that each of them is decisive in a way and determines the ability to build and the performance of the final system. A network of communication nanoparticles can cover a wider area and perform more network processing . In addition, there are many nano telecommunication technologies that require the use of external stimulation and measurement to work. Wireless communication between nano network and micro and macro devices and equipment can meet this need.
In general, in order to receive the electromagnetic wave in the space, the dimensions of the antenna must be in the same order as the wavelength of the input to its surface. Due to the very small dimensions of nano sensors, nano antennas need to have a very high working frequency to be usable. The use of graphene helps to solve this problem to a great extent. The speed of propagation of waves in CNTs and GNRs can be 100 times lower than its speed in vacuum, and this is related to the physical structure, temperature and energy. Based on this, the resonance frequency of graphene-based nano-antennas can be two times lower than nano-antennas based on nano-carbon materials. It has been mathematically and theoretically proven that a quasi-metallic carbon nanotube can emit terahertz radiation when a time-varying voltage is applied to its sides. Despite the possibilities of making nanotubes with a length of several centimeters, it is possible There is the construction of electrical conductors with a ratio of length to width of the order of 10^7 . At first glance, nanotube antennas give us the impression that they are similar to Dipole antennas designed in small dimensions. But in fact, it is not the case in the main theory of Dipole antennas to determine the distribution of current on the antenna, where the Dipole radius is larger than the skin depth and also the resistance losses are so low that they can be ignored.
Conclusion :
The efficiency of a classic nanotube antenna is around -90dB, which is due to resistive losses.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics