All molecular-based electrochemical nano-sensors depend on a highly specific system for detecting or tracking target molecules (PhD in Nano-Microelectronics)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
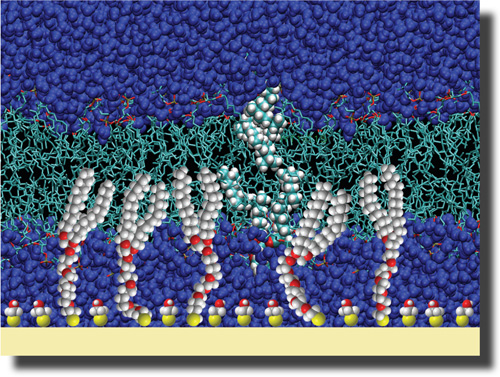
Note: All molecular-based electrochemical nano-sensors rely on a highly proprietary system to detect or track their target molecule. The importance of an electrochemical nano-sensor is to provide a suitable support for attaching the target molecule to the probe and generating an electrical signal that can be measured and read.
In the construction of electrochemical biosensors, the minimum parts used in a biosensor are the layer recognition molecular and the signal transducer that can be connected to a device readout of these signals. DNA is usually a good tool as a biosensor because the base pairing reaction between complementary play sequences is both specific and stable. In this case, the single-stranded probe DNA is immobilized on the detection layer and then reacts with the probe on the surface by pairing the target DNA. The duplication and unitary nature of DNA structures determines their accumulation on the surface. It is on this surface that the target DNA is captured and a signal is generated. Therefore, immobilizing the nucleic acid of the probe While maintaining its original adhesion strength, it is important to detect target DNA. But how this diagnostic procedure is measured depends on the method of the transduction signal, which may be optical, mechanical, or electrochemical. Optical biosensors based on fluorescent light have features. These types of biosensors are sensitive to molecules per square centimeter. They consist of rows that are ٧ so that their detection limit is made up of almost thousands of probes. Because the tools in this field (fluorescence biosensor) are complex and expensive . Gene chips technology is more suitable for laboratory work. Gene chips in cases where a lot of work needs to be done at the same time, such as profiling transcriptional profile or poly checkDiscovery polymorphism nucleotide Single may be appropriate, but clinical diagnoses usually do not require the collection of much data. What is important for molecular diagnosis is the reliability of the diagnosis as well as its generality regardless of the order of the game. Therefore, gene chips are not preferred for clinical diagnosis for reasons such as: expensive and complex device. Also for other specific reasons, reading accuracy is reduced. Another method for measuring the signal optically is the superficial plasmon resonance method ( Resonance Plamon Surface) In this method, the refractive index of a thin metal film substrate is changed, which is due to the absorption of analyte and is suitable for detecting the target in situations where the house is a groove groove. because In this method, we can reach the detection limit of the target molecule at which the signal is generated. The hybridization signal must be amplified. This can be enhanced by increasing the amount of material on the film surface before or after binding to the target DNA. The resonant Plus ون surface (SPR) method is similar to the expensive and complex fluorescence method, which is why it is so expensive and complex that it is used more for research work than for routine diagnostic work ; One method of measuring the signal by light, which is very clear, is the light reading method, in which single-stranded DNAs are labeled with gold nanoparticles, which easily change color due to hybridization in the order of the target game . Using silver staining, DNA analysis can be performed with this optical method on very small plates with sensitivity. Although the use of gold nanoparticles may be expensive, this method has the sensitivity and simplicity necessary for clinical diagnoses.
One way to read or measure a signal is to measure changes in the immobilized detection layer that result from binding to a target molecule. In this case, Quartz Microbalance Crystal is mostly used. This device is sensitive and can report hybrid production (mating) at the time of its formation. One of the limitations of the QMC method is that this method can not be done when the target sample is in the soluble phase, but with advances in this area, ie the creation of new methods of propagation and amplification of the sample may be removed this limitation. Another method of volumetric measurement is the use of Cantilevers Microf bricated method. In this method by increasing the volume that accompanies the hybridization by The laser beam is detected from the surface of the cantilever. One of the advantages of this method is its suitability for developing linear grooves and that this method can correct non-specific connections. One of the disadvantages of this method is the high cost and complexity of the tools and devices used. Electrochemical methods are very suitable for DNA detection because electrochemical reactions directly generate electronic signals and therefore do not require expensive converters. In addition, because the order of the immobilized game can be limited to a single set of electrode substrates, the tracking operation can be performed by a series of inexpensive electrochemical analyzes . Electrochemical sensors for on-site clinical or environmental testingIs provided. The basis of the sensitivity of electrochemical signals to direct oxidation or catalysis of DNA bases is also the reduction reactions of reporter molecules or enzymes. Various methods are used to measure the signal electrochemically. The basis of signal measurement in direct DNA electrochemistry is based on the oxidation reaction and DNA reduction at a mercury electrode , so the amount of oxidized and reduced DNA is proportional to the amount of DNA hybridized with the probe. In addition to the old methods of direct DNA reduction, today a method called absorption voltammetry of surface nanomolecules (Stripping Adsorption Voltammetry) is used to select nanomolecules for direct oxidation of DNA, which is a very sensitive method. In the methodDirect electrochemistry of purine bases is oxidized by materials such as carbon, indiomethin oxide (ITO) gold and polymer -coated electrodes . Although the direct electrochemical method is a very sensitive method, its application is complex.
Conclusion :
All molecular-based electrochemical nanosensors rely on a highly proprietary system to detect or track their target molecule. The importance of an electrochemical nano-sensor is to provide a suitable support for attaching the target molecule to the probe and generating an electrical signal that can be measured and read.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
PhD in Nano-Microelectronics