_ electronic memory part (C _ MOS) CMOS
bitstream and configuration electronic memory (C_Mouse) CMOS
Researcher and author: Dr. Afshin Rashid
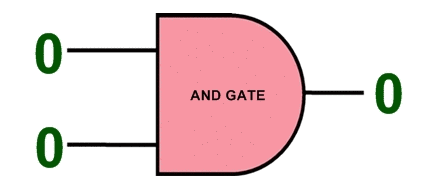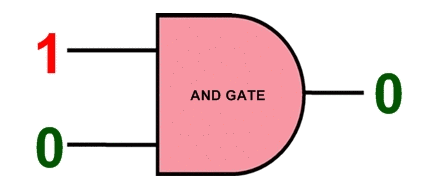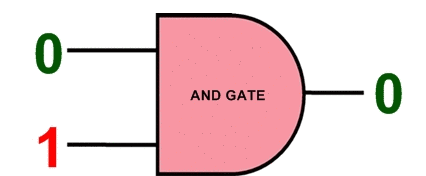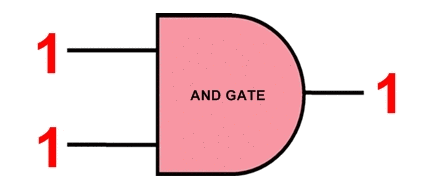
Note: configuration information in electronic memory (C_Mouse) CMOS in configuration memory cells is saved. Instead of using a RAM block for storage, Electronic memory (C_Mouse) CMOS is distributed across the chip in a 71 x 160 grid, ensuring that each bit is next to the circuit it controls. a configuration bitstream in electronic memory (C_Mouse) CMOS loading will be The bit stream is fed to the shift register that runs through the center of the chip (pink). When the 71 bits are loaded into the shift register, the selection circuit selects a particular column of memory and the bits are loaded into this column in parallel. Then the next 71 bits are loaded into the shift register.This process for all 160 columns (C _ Mouse) < /span> Iterates and loads the entire bitstream into the chip.CMOS
Since CMOS electronic memory work in parallel, they have a much higher speed and therefore can be They are used to solve complex computational problems, along with reprogrammability - this makes CMOS electronic memory (CMOS) powerful machines. and be flexible. The important point is that the bitstream is distributed across the chip exactly as it appears in the file: the arrangement of bits in the bitstream file corresponds to the physical layout on the chip a i=6>, each bit is stored inCMOS electronic memory next to the circuit it controls. Thus, the bitstream file format is directly determined by the hardware circuit design. For example, when there is a gap between the memory lines of CMOS electronic memory due to the buffer circuit. Yes, the same gap appears in the bit stream. Bitstream content is not designed around software concepts such as fields or data tables or configuration blocks.
Memory resources are another key specification to consider when choosing CMOS electronic memory . User-defined RAM, embedded across the CMOSchip, to store data sets Or passing values between parallel tasks is useful. Depending on the CMOS family, you can electronic memory ( Configure CMOS in 16 or 36 KB blocks. Digital signal processing algorithms often need to keep track of an entire data block or multiples of a They have a complex equation and no internal memoryCMOS electronic memory allows independent pieces of hardware logic to be driven by different clocks. Transferring data between logic running at different speeds can be difficult, and internal memory is often used to smooth the transfer using first memory buffers.
While there are many advantages such as speed, reliability, and flexibility to CMOS electronic memory , the trade-off There are also some with FPGAs. CMOS electronic memory do not have the drive ecosystem and code/IP base that microprocessor architectures and operating systems have. Furthermore, microprocessors, along with operating systems, provide the basis for file structures and communication with peripheral devices used for many, often essential, tasks, such as recording data to disk. a>This approach takes advantage of the advantages that both of these goals offer.As a result, over the past decade, a hybrid architecture, sometimes called a heterogeneous architecture, has emerged in which a microprocessor is paired with an FPGA, which then connects to the I/O. Modern CMOS electronic memory often combines logic gates with processors on a single chip called a System on Chip (SoC) to increase They combine computing performance.
Researcher and author: Dr. Afshin Rashid
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics