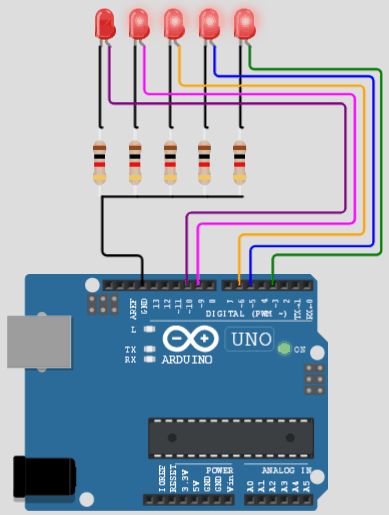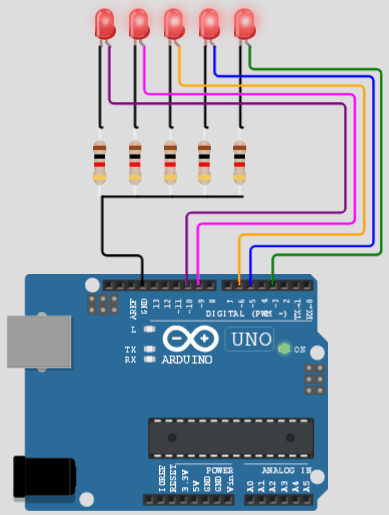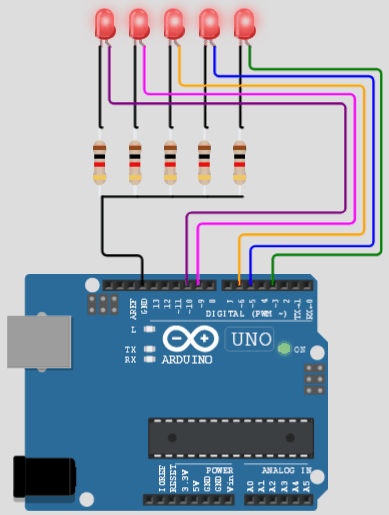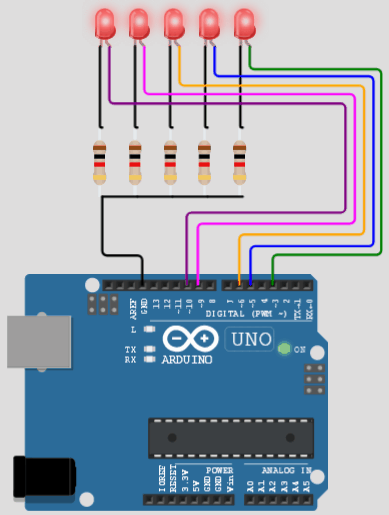
_ بخش دیود های LED (دیود های نورانی)
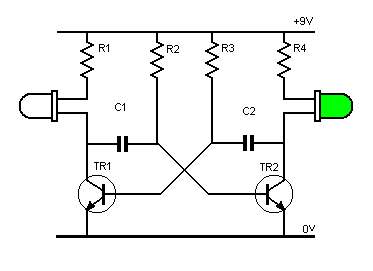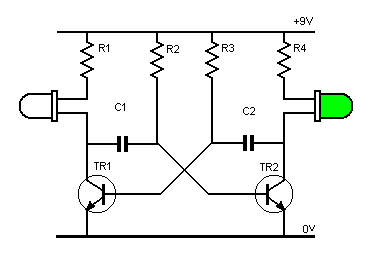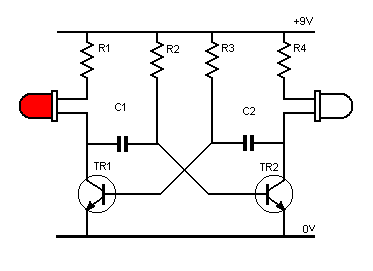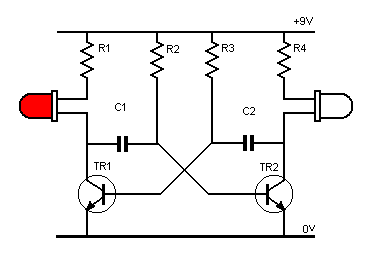
آز مدار اِلکترونیکی با دیود های LED یا (دیود نور اَفشان)
پژوهشگر و نویسنده: دکتر ( افشین رشید)
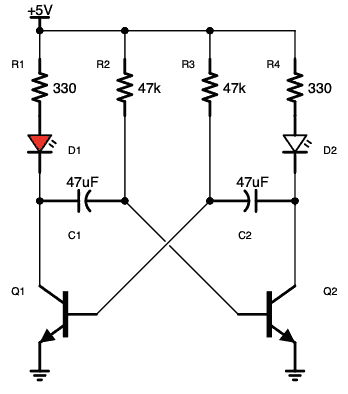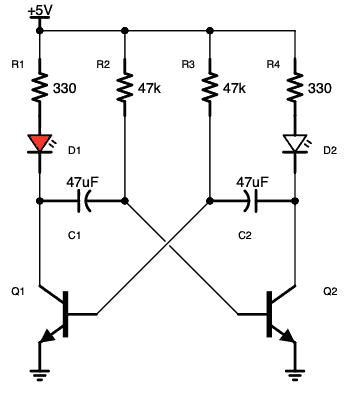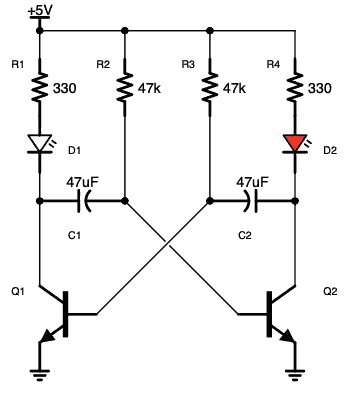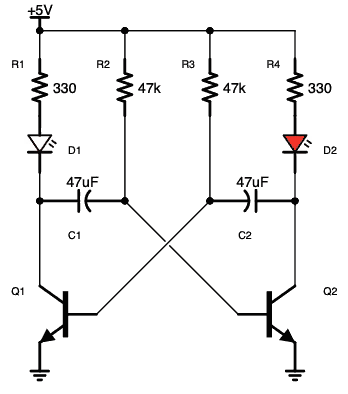
نکته: در مدارات الکترونیکی دیود های LED بارزترین نوع دیود هستند ، که از یک پهنای باند نسبتاً باریک از هر دو نور مرئی در طول موج های مختلف رنگی ، نور مادون قرمز نامرئی برای کنترل از راه دور یا نوع لیزر نوع در هنگام عبور یک جریان رو به جلو از آنها ساطع می کنند.
" دیود نورانی" یا همان LED که معمولاً از آن یاد می شود ، در واقع فقط یک نوع دیود تخصصی است زیرا مشخصات الکتریکی بسیار مشابهی با یک دیود اتصال PN دارند. این بدان معنی است که یک LED جریان را در جهت رو به جلو خود عبور می دهد اما جریان جریان را در جهت معکوس مسدود می کند.
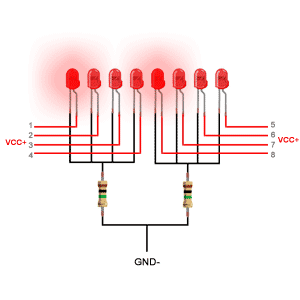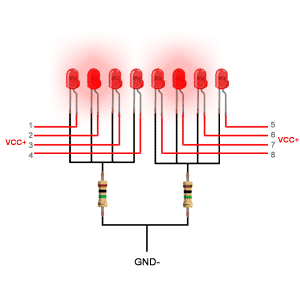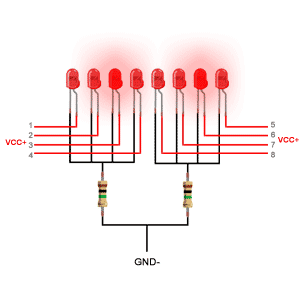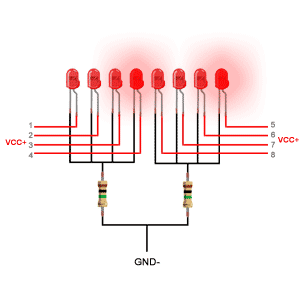
دیودهای ساطع کننده نور از یک لایه بسیار نازک از ماده نیمه هادی نسبتاً دوپ شده ساخته شده و بسته به نوع ماده نیمه هادی مورد استفاده و میزان دوپینگ بستگی دارد ، هنگامی که به سمت مغایر قرار گیرد ، یک چراغ رنگی را در طول موج طیفی خاص منتشر می کند.
فقط (دیود نور اَفشان) بایاس رو به جلو اجازه می دهد تا جریان در آن جاری باشد، در نتیجه نور LED را روشن می کند، دیود بایاس معکوس اجازه نمی دهد هیچ جریانی از آن عبور کند.
دیودهای منتشر کننده نور از وسایل نیمه هادی هستند که انرژی الکتریکی را به انرژی نور تبدیل می کنند.رنگ واقعی یک دیود ساطع کننده نور با طول موج نور ساطع شده تعیین می شود ، که به نوبه خود توسط ترکیب نیمه هادی واقعی مورد استفاده در شکل گیری اتصال PN در طول تولید تعیین می شود. بنابراین رنگ نوری که توسط یک LED ساطع می شود با رنگ آمیزی بدنه پلاستیکی LED مشخص نمی شود ، هرچند که این مقادیر کمی رنگ هستند که هم باعث افزایش نور می شوند و هم در هنگام روشن نبودن منبع برق ، رنگ آن را نشان می دهند.دیود های LED محدوده کاری تقریباً از 1.2 تا 3.6 ولت دارند و دارای جریان فعلی رو به جلو در حدود 10 تا 30 میلی آمپر است که 12 تا 20 میلی آمپر آن رایج ترین محدوده است.ولتاژ عملیاتی رو به جلو و جریان رو به جلو بسته به ماده نیمه هادی مورد استفاده متفاوت است.
LED ها (دیودهای انتشار نور) منابع نوری نیمه هادی هستند که یک نیمه هادی از نوع P (غلظت سوراخ بزرگتر) را با یک نیمه هادی از نوع N (غلظت الکترونی بزرگتر) ترکیب می کنند. اعمال ولتاژ رو به جلو کافی باعث می شود الکترون ها و سوراخ ها در محل اتصال PN نو ترکیب شوند و انرژی را به صورت نور آزاد می کنند. در مقایسه با منابع نوری معمولی که ابتدا انرژی الکتریکی را به گرما تبدیل می کنند و سپس به نور تبدیل می شوند ، LED ها (دیودهای ساطع کننده نور) انرژی الکتریکی را به طور مستقیم به نور تبدیل می کنند و تولید برق کارآمد با انرژی کم مصرف می کنند.دو نوع LED وجود دارد ، یک نوع لامپ (سرب) و نوع تراشه (سطح نصب شده). کاربران می توانند بر اساس نیاز مجموعه ، نوع ایده آل را انتخاب کنند.
یک توضیح ابتدایی (یادآوری) درباره (دیود نور اَفشان) دیود ال _ ای _ دی LED
LED مخفف Light- Emiting Diode (دیود نورانی) میباشد. این اِلمان نوعی دیود است که وقتی جریان خود را از درون خود جریان می دهد ، نور را ساطع می کند.LED ها نوعی نیمه هادی به نام "دیود تابش نور" هستند. LED های سفید که با استفاده از LED های آبی روشنایی بالا که بر اساس ماده گالیم نیترید ساخته شده اند ، به عنوان یک منبع نور 4 نوع نور زرد، آبی، سبز ، قرمز از خود ساطع می کنند
پژوهشگر و نویسنده: دکتر ( افشین رشید)
دکترایِ تخصصی نانو _ میکرو الکترونیک