Section _ reproduction and production of nanowires
Using Scanning Nano Lithography in the immersion method of nanowires
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
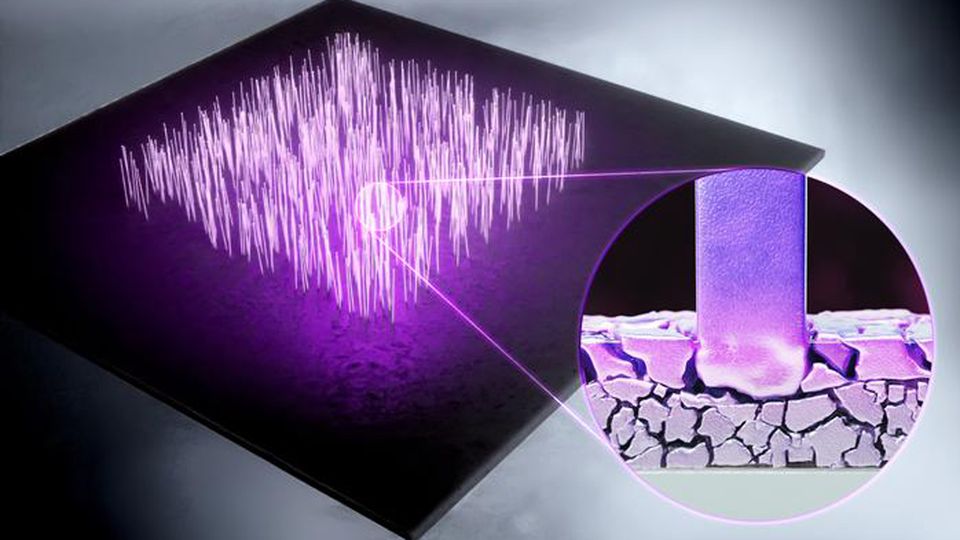
Note: Many possible applications of nanoscale modifications with thermal probes such as Robeshi nanolithography or (Scanning Nano Lithography) are still applicable in nanoelectronics, especially when ultra-high heating and cooling rates can be used to produce nanowires. used
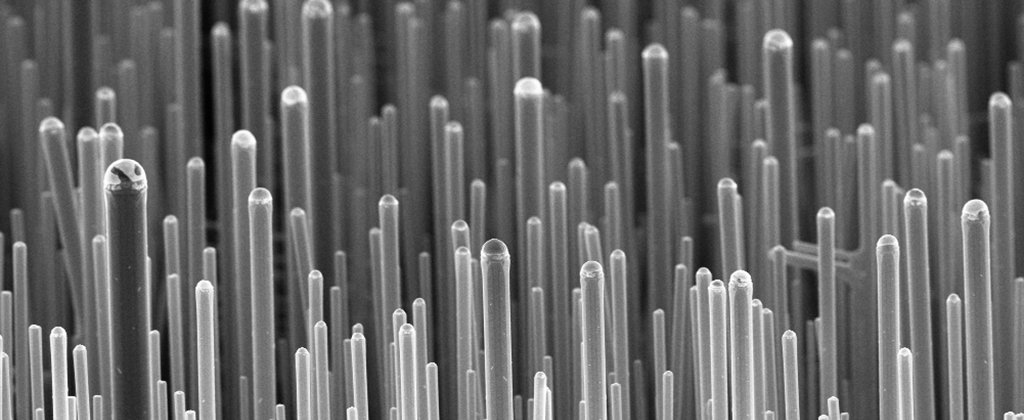
Many microsystems and nanosystems require precise nanoscale patterns that exhibit intrinsic functionality, such as some electronic, photonic, chemical, and mechanical properties. To fabricate these nanoscale patterns, electron beam lithography is the most common lithography technique without direct writing and without masks. Scanning Nano Lithography requires a complex electron compatible light to focus the electron beam into a spot of a few nanometers. Another issue is electron scattering, a type of proximity effect, on the sample surface, which leads to the exposure of additional unwanted resistivity that must be corrected by intensive calculation algorithms. Scanning Nano Lithography is another method of direct writing nanolithography, where patterns are created by scanning a nanometer tip on the sample to create local changes. Sample-sample interactions are numerous and can include mechanical, electrical, diffusion, and thermal effects.
_crlk.gif)
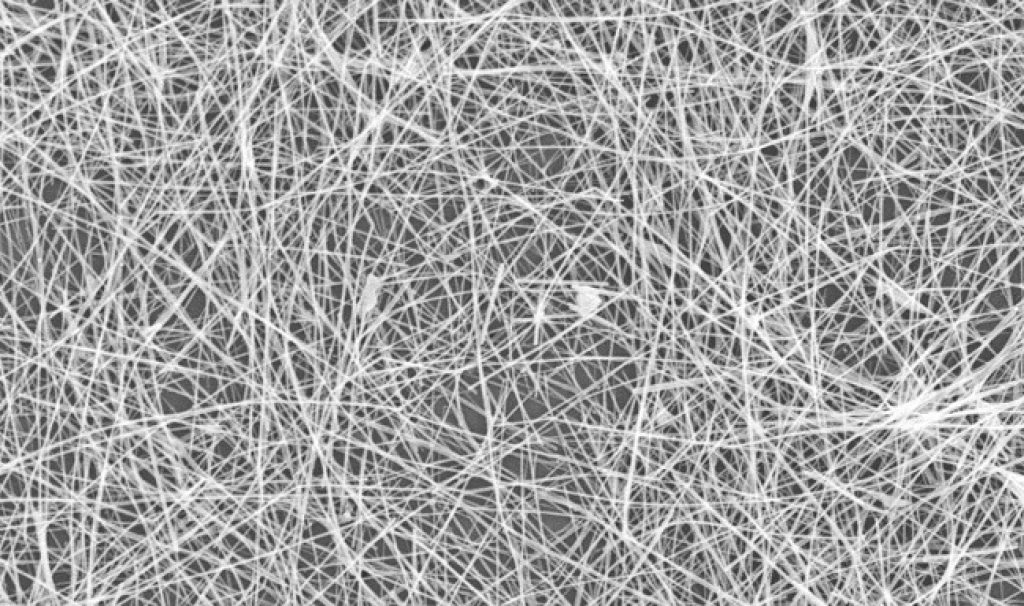
In the immersion method, the nanowires have enough time to transfer from the particles of the nanowires to the holes; The step of forming uniform nanoparticles is done slowly and finally uniform nanowires are formed. Structural investigation with FESEM in the immersion method of uniform nanowires in all disorders and in a wide area in nanowire particles. By changing the Sr/Fe ratio, there is no change in the morphology of the nanowires. and the spectroscopy of nanowires with different Sr/Fe ratios inside the internal nanoparticles (uniform nanowires), the presence of Fe and Sr elements is caused by strontium ferrite, in the spectroscopy of uniform nanowires, it is observed that the ratio of Sr/Fe nanoparticles to the amount Its stoichiometry in the electromagnetic composition of nanoparticles is closer, while due to the lower solubility of strontium uniform nanowire nanomolecules compared to iron nitrate and the presence of less strontium ions in the reaction with the electromagnetic particles of nanowires, There is a higher amount of Fe ion in the final structure.
To separate uniform nanowires, molar electromagnetic active particles are used at ambient temperature . In the application of nanowires in nanoscale electronic devices or some other applications, it is necessary to separate nanowires from alumina particles .
Conclusion:
Many potential applications of nanoscale modifications with thermal probes such as scanning nanolithography are still applicable in nanoelectronics, especially when ultra-high heating and cooling rates can be used to produce nanowires. .
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics