_ Nanoreactors and (nanostructures) section
One of the main applications of nanoreactors is in the electronic conduction of porous materials whose dimensions are smaller than 0.11 nanometers.
Researcher and Author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Note: In general, nanoreactors can be divided into two groups: natural and synthetic nanoreactors. The first group has a more selective function and at the same time a more complex structure, while the second group has more diversity and a simpler structure. Natural nanoreactors Cells and cellular organelles, which are considered the most ideal nanoreactors, have lipid membranes.
These nanoreactors are selective, meaning they are able to distinguish between different molecules and allow only certain molecules to enter their internal cavity. In addition to selectivity, cells are also sensitive by having pores in the membrane that open and close with external stimuli such as pH changes. Selectivity and sensitivity are characteristics of all natural nanoreactors and are used in the production of nanosensors.
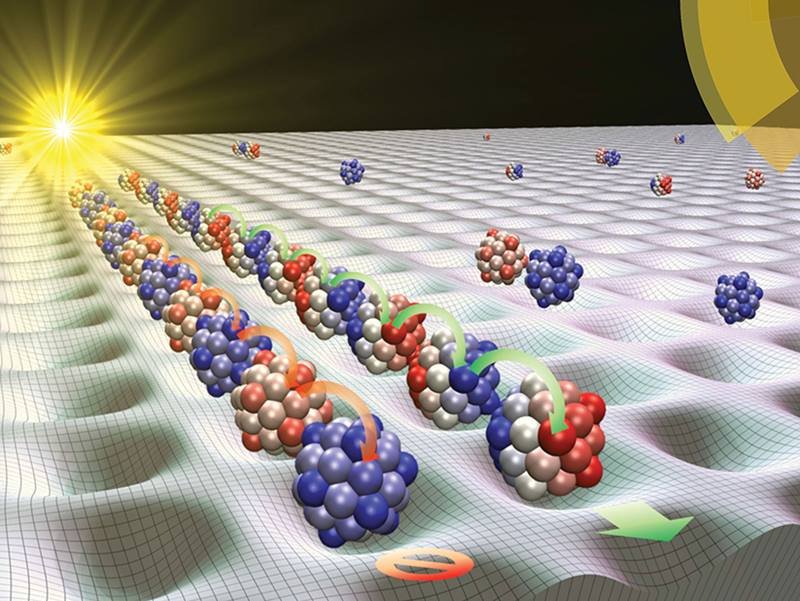
Nanoreactors are very diverse. Simple or complex, organic and inorganic materials with electrical conductivity, volume and pore structures are used as nanoreactors. Unlike microreactors, the reaction space inside nanoreactors greatly affects the mobility and interactions between molecules inside it. Therefore, a nanoreactor is not just a simple storage container and plays an important role in the electrochemical process. Nanoreactors are relatively new materials, but in nature, various processes have long been using nanoreactors. Performing electrochemical reactions in confined spaces with nanometer dimensions and micrometer volumes leads to changes in the kinetics and path of the entire process. Such confined spaces used to perform specific electrochemical reactions are called nanoreactors. Nanoreactors are very small containers with nanometer dimensions that have great potential for improving electrochemical conversions by protecting catalysts from environmental effects and confining reactants and catalysts in a small space for a long time . In fact, nanoreactors are porous materials with one of their dimensions being on the nanoscale.