Method of studying the structure of Nano wire electrons (based on nano-micro-electronics PHD)
Researcher and author : Dr. Afshin Rashid
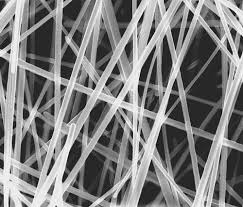
![]() Note: A nano-SIM is a very thin wire with a diameter of the order of a few nm (nanometers) or less, where 1 nm = 10 -9 meters. The two processes in nanotechnology technology by which nanowires can be produced are suspension.
Note: A nano-SIM is a very thin wire with a diameter of the order of a few nm (nanometers) or less, where 1 nm = 10 -9 meters. The two processes in nanotechnology technology by which nanowires can be produced are suspension.
A Nano SIM Nano wire suspended at one end in a discharge chamber is kept and then reducing atoms or molecules of high-speed chemically bombarded to reduce its diameter. Other methods include drilling the surface of the wire in the center of the suspended opening, raising the temperature, and then pulling the wire while it is near its melting point. A sedimentation nanowire is made on a surface composed of some non-conductive materials such as plastic or glass. This process is similar to the way their semiconductor chips grow.
Nano-wire is a two-dimensional structure and is also known as quantum wire due to its quantum effects. Nano-wires are made of metals and semiconductors and various types of polymers and can be used in the preparation of very small electrical circuits, including computers and computing devices, etc. In the presence of chemicals, they change, so these nanowires are used in the manufacture of sensors to detect chemicals, including gases. Nanofibers can be used to detect or absorb radio waves. Also, nanoscale laser diodes can be easily obtained by connecting two different types of nanowires.
Ordinary Nano wire nanoparticles show dimensional ratios (length-to-width ratios) of 1000 or more. As such, they are often referred to as 1D materials. Nanochemicals have many interesting properties that are not found in bulk or 3D materials. This is because the electrons in the nanowires are quantum, which is limited on the side and therefore occupies the energy level, which is different from the traditional energy level layer or bands present in bulk materials.
Conclusion:
Nanosystems show their ability to break down electrical conduction values. These discrete values are due to the quantum mechanical limitation on the number of electrons that can pass through the wire on a nanometer scale. These discrete values are often referred to as conductive quantum