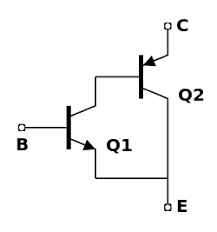
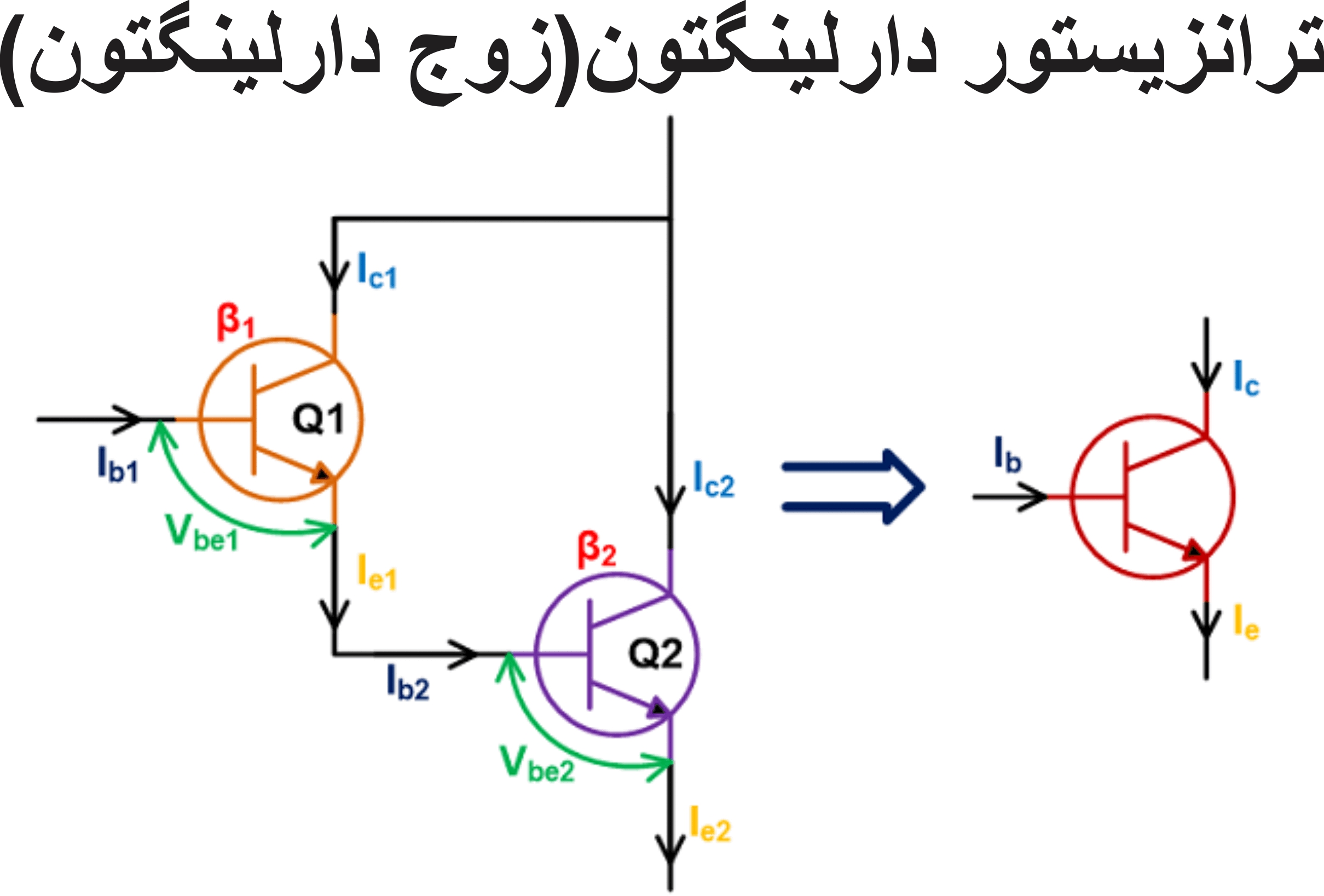
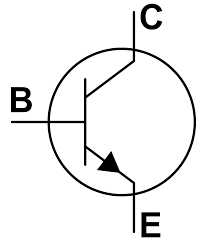
Section _ Understanding (Darlington transistor ) or Darlington pair
Investigation of the intrinsic gap ratio (η) for (relaxation and trigger mechanisms) in the Darlington transistor Darlington = pair or pair
Researcher and Author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
_60js.png)
A Darlington transistor operates based on a unique mechanism characterized by a negative resistance region, which is crucial for its applications, particularly in relaxation oscillators. This behavior of a Darlington transistor is controlled by the internal structure of the device and the interaction of voltage and current in its layers, which is distinct from standard bipolar junction transistors (BJTs).
Examining the intrinsic gap ratio (η) in a Darlington transistor :
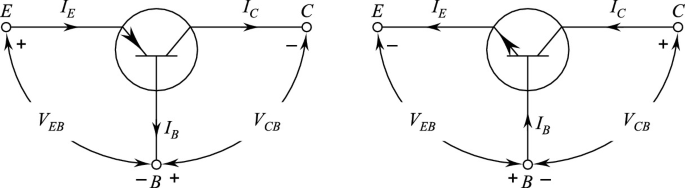
This parameter is very important for determining the firing voltage (Vp) for a Darlington transistor . This voltage is a fraction of the voltage between the bases, calculated as R_B1/(R_B1 + R_B2), where R_B1 and R_B2 are the resistors between the emitter and the respective bases.
The intrinsic gap ratio (η) plays a fundamental role in the performance of a Darlington transistor , a critical parameter that determines the firing voltage (also known as the peak point voltage (Vp), the voltage at which the device switches from off to conducting. The emitter-base junction in a Darlington transistorexhibits nonlinear behavior where increasing the emitter voltage beyond Vp results in a decrease in the emitter resistance, exhibiting the aforementioned negative resistance characteristic.
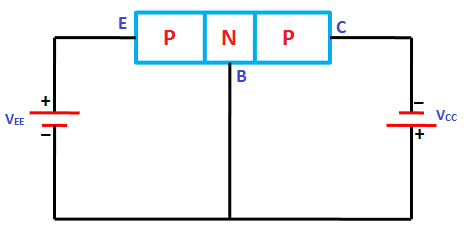
The operating cycle of a Darlington transistor begins with the emitter junction reverse biased, essentially acting as an open switch. When the voltage at the emitter reaches the peak voltage (Vp), the emitter junction becomes forward biased due to the modulation of the conductivity of the silicon rod, injecting current into the base region. This transition causes a Darlington transistor to enter the conducting state until the emitter current drops below the valley current, at which point it returns to its high resistance state. This cycling behavior is what makes a Darlington transistor suitable for relaxation oscillators and trigger mechanisms.