Gas nanoparticles with carbon nanotubes and carbon-based electrical conductivity based on nanotechnology- microelectronics PHD (educational-research doctorate)
Researcher and author PhD student : Afshin Rashid
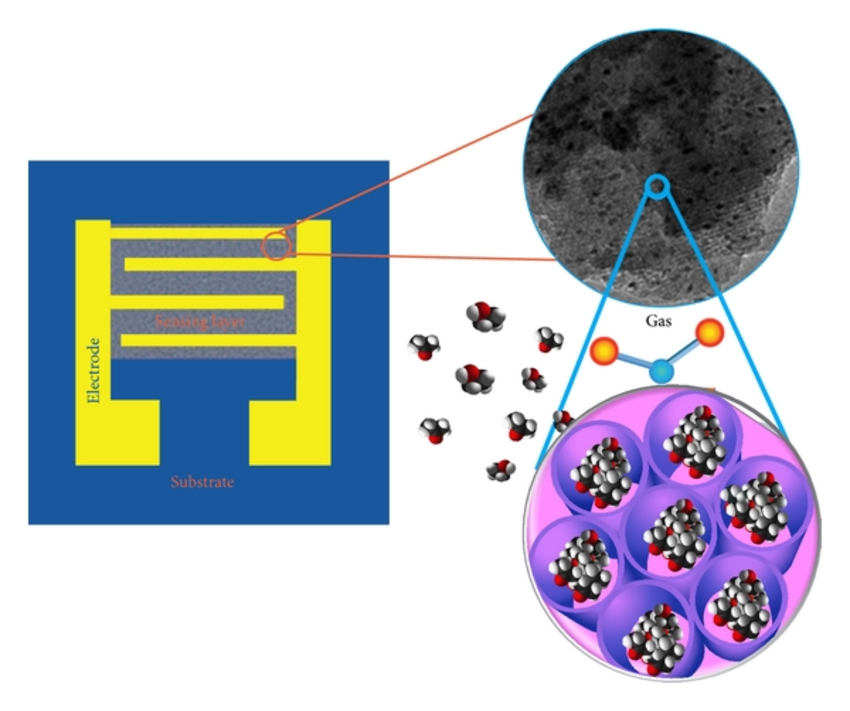
Note: The various properties of carbon nanotubes, such as optical and electrical properties, have led to the use of these materials to make sensors. Gas nanosensors whose electrical current changes as a result of the presence of the target material.
In these sensors, the carbon block is dispersed inside an insulating polymer, thus providing electrical guidance to the film. If the gas / steam is present, the polymer swells and eventually the electrical conductivity / resistance of the polymer changes. Using a suitable solvent, the viscosity of the carbon black polymer / carbon is adjusted appropriately, and then the polymer is modeled on the surface of the filter electrode. Different methods, such as spinning and drip coating, are applied to place the polymer on the surface of the electrodes, and eventually the coating dries. The changes in electrical conductivity in gas nanosensors are based on the percentage of carbon black.
If the amount of carbon black carbon in the nano sensor is low, the composite will be insulated, which is due to the lack of connection between the conductive particles in the body of the composite. As the amount of carbon in the polymer increases, the electrical resistance of the polymer decreases exponentially. By increasing the carbon block concentration and reaching the transfer point, the connection is established based on the penetration limit. If the intended vapor / gas is present, the polymer swells and the amount of conductivity / electrical resistance changes, this change is used to identify the gas.
Conclusion:
In gas nanoparticles with carbon nanotubes and carbon-based electrical conductivity, the electrical resistance signals are removed from these arrays and evaluated using a standard system. And the goal is to be able to identify different vapors of organic solvents in person. This strategy can be combined with various software and hardware systems, and ultimately polymer / carbon composite sensors may be delayed due to the matrix of polymer matrix or the displacement of carbon black particles in response to external stimuli . Changing the location of particles or matrix aging changes the path of penetration. This arrangement changes as a result of swelling and wrinkles Repeated washing of the polymer matrix occurs due to repeated use of the sensor.
Author: PhD Student ( Afshin Rashid)