_ بخش حافظه اِلکترونیکی (سی _ موس) CMOS
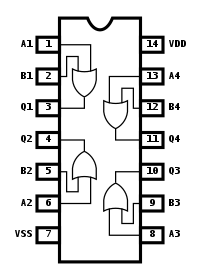
حافظه NOR در ic های حافظه اِلکترونیکی (سی _ موس) CMOS
پژوهشگر و نویسنده: دکتر ( افشین رشید)
نکته: حافظه NOR در ساختار حافظه اِلکترونیکی (سی _ موس) CMOS یکی از دو نوع فناوری ذخیره سازی غیر فرار است. دیگری است. حافظه غیر فرار برای نگهداری داده ها نیازی به برق ندارد.ic آیسی های حافظه اِلکترونیکی (سی _ موس) CMOS NOR و NAND از گیتهای منطقی متفاوتی برای برنامه ریزی استفاده می کنند - بلوک ساختمانی اساسی مدارهای دیجیتال - در هر سلول حافظه برای نقشه برداری داده ها.
خواندن حافظه NOR سریع تر از حافظه NAND است، اما گران تر است و پاک کردن و نوشتن دادههای جدید بیشتر طول می کشد. NAND ظرفیت حافظه بالاتری نسبت به NOR دارد. حافظه اِلکترونیکی (سی _ موس) CMOS در دستگاه های حافظه NAND بهصورت سریالی، با استفاده از همان هشت پین برای انتقال اطلاعات کنترل، آدرس و داده، قابل دسترسی هستند. NAND می تواند در یک آدرس حافظه واحد بنویسد، این کار را در هشت بیت - یک بایت - در یک زمان انجام می دهد.
حافظه اِلکترونیکی (سی _ موس) CMOS از نوع NOR قدیمی تر از دسترسی تصادفی یک بایتی پشتیبانی می کند. این امر امکان بازیابی و اجرا مستقیم دستورالعمل های ماشین را از تراشه فراهم می کند - به همان روشی که یک کامپیوتر سنتی دستورالعملها را مستقیماً از حافظه اصلی بازیابی می کند. با این حال، NOR باید در تکه های بزرگتر از داده در یک زمان از NAND بنویسد.
حافظه اِلکترونیکی (سی _ موس) CMOS و حافظه داخلی NOR موازی دارای یک رابط حافظه با دسترسی تصادفی استاتیک (SRAM) است که شامل پین های آدرس کافی برای نقشه برداری از کل تراشه است و امکان دسترسی به هر بایت ذخیره شده در آن را فراهم می کند.همچنین تولید فناوری فلش NOR گرانتر است و هزینه هر بیت بالاتری نسبت به NAND دارد. این و تابع دسترسی تصادفی آن، میانگین NOR بیشتر برای اجرای کد استفاده می شود، در حالی که حافظه فلش NAND بیشتر برای ذخیره سازی داده ها استفاده می شود.وقتی صحبت از مصرف انرژی به میان می آید، حافظه فلش NOR در اولین روشن شدن به جریان برق بالاتری نسبت به NAND نیاز دارد. با این حال، پس از روشن شدن، نیاز برق آماده به کار برای NOR بسیار کمتر از NAND است. بنابراین، NOR به طور کلی برای خواندن تصادفی از حافظه بهتر است، در حالی که NAND در نوشتن، پاک کردن و خواندن متوالی کارآمدتر است (حافظه اِلکترونیکی (سی _ موس) CMOS و قسمت حافظه NOR) عمر بی نهایتی ندارد. اعمال میدان های ولتاژ بالا در نهایت باعث تخریب ترانزیستورها می شود، که به این معنی است که گیت های شناور زمان بیشتری برای کار کردن خواهند داشت. با این حال، بسیاری از انواع فلاش تا حداقل 10000 بازنویسی شروع به کند شدن نمیکنند، و میتوانید این ویرایشها را در کل تراشه توزیع کنید تا تأثیر عملکردی فرسودگی را محدود کنید و کاربرد را برای مدت طولانیتری حفظ کنید.
پژوهشگر و نویسنده: دکتر ( افشین رشید)
دکترایِ تخصصی نانو _ میکرو الکترونیک