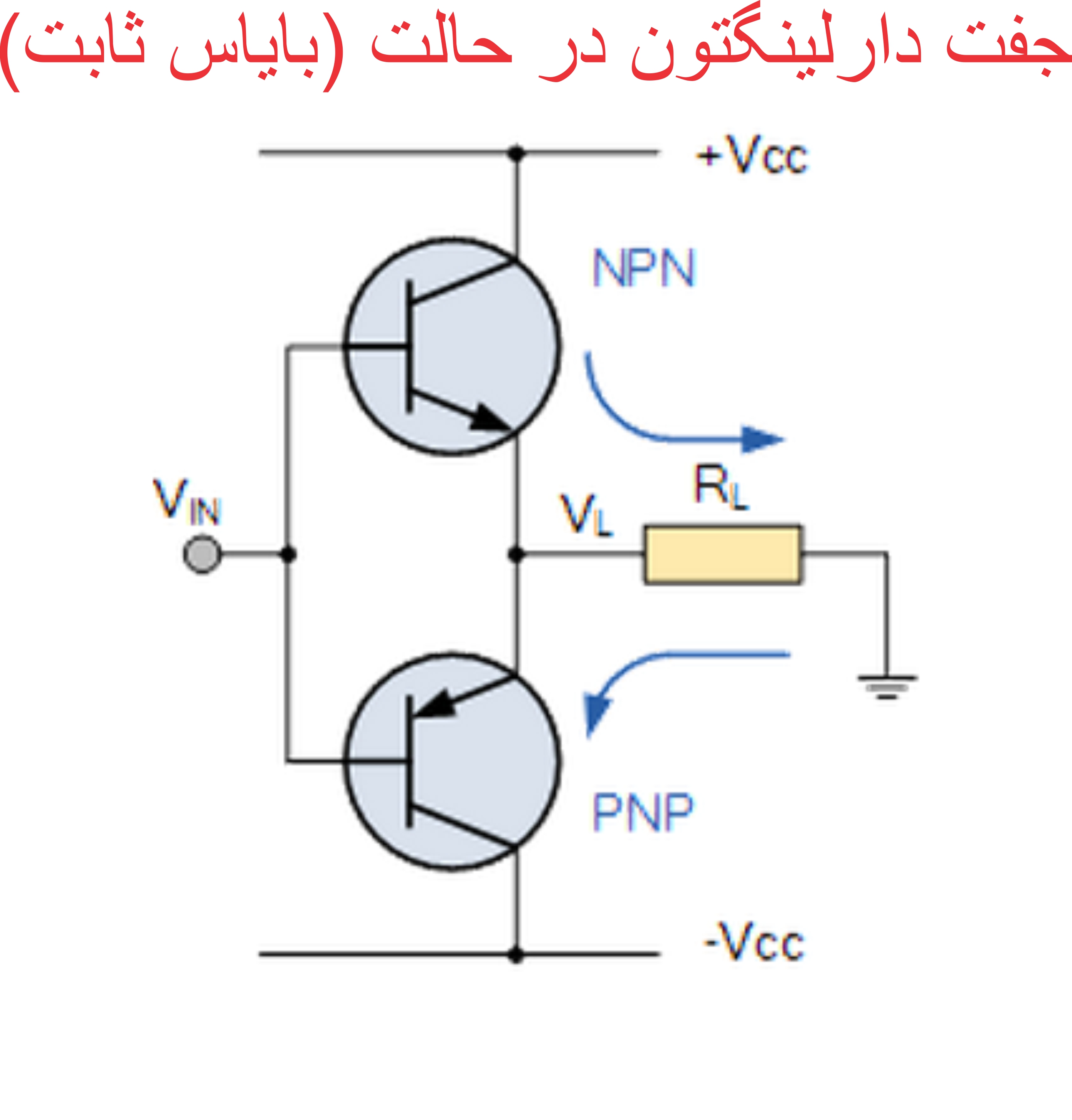
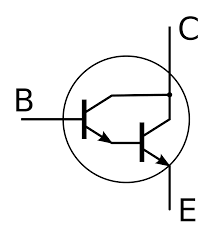
Section _ Understanding (Darlington transistor ) or Darlington pair
(Constant bias) mode in Darlington transistor Darlington (Darlington pair) = (Darlington pair)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
For a Darlington transistor to operate properly , it is necessary to apply external voltages of the correct polarity to its emitter-base and collector-base junctions. This biasing of the Darlington transistor is called biasing . In electronics, biasing is the adjustment of the initial operating conditions (current and voltage) of an active component in an amplifier. Many electronic components, such as diodes, transistors, and vacuum tubes, whose function is to process time-varying (AC) signals, also require a constant current or voltage (DC) at their terminals to operate properly. This current or voltage is called bias . The AC signal applied to them is superimposed on this DC bias current or voltage.
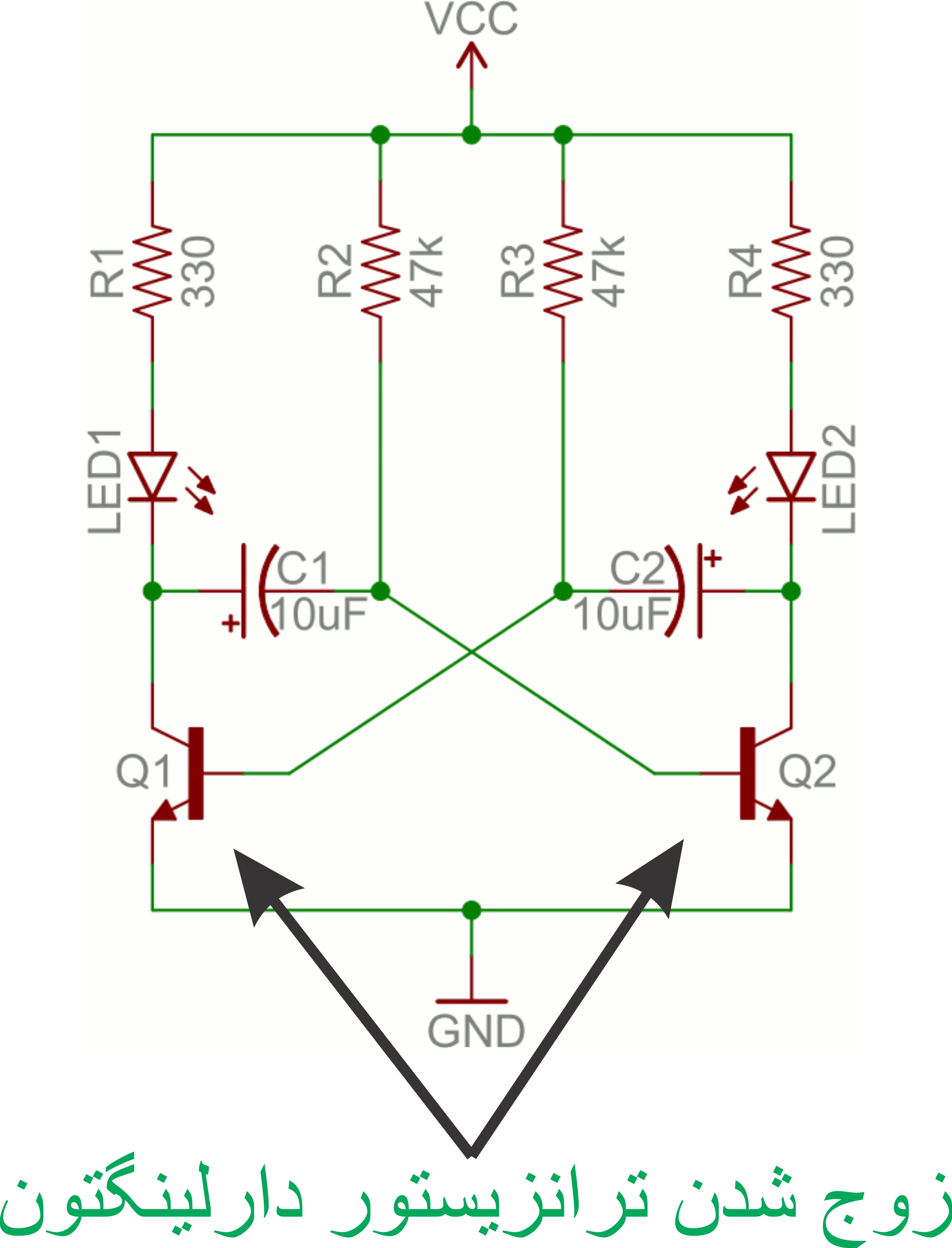
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized PhD in Nano-Microelectronics