Section _ Understanding (Darlington transistor ) or Darlington pair
Darlington transistor (Darlington pair) A special arrangement of two modes, NPN and PNP
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
_ife5.gif)
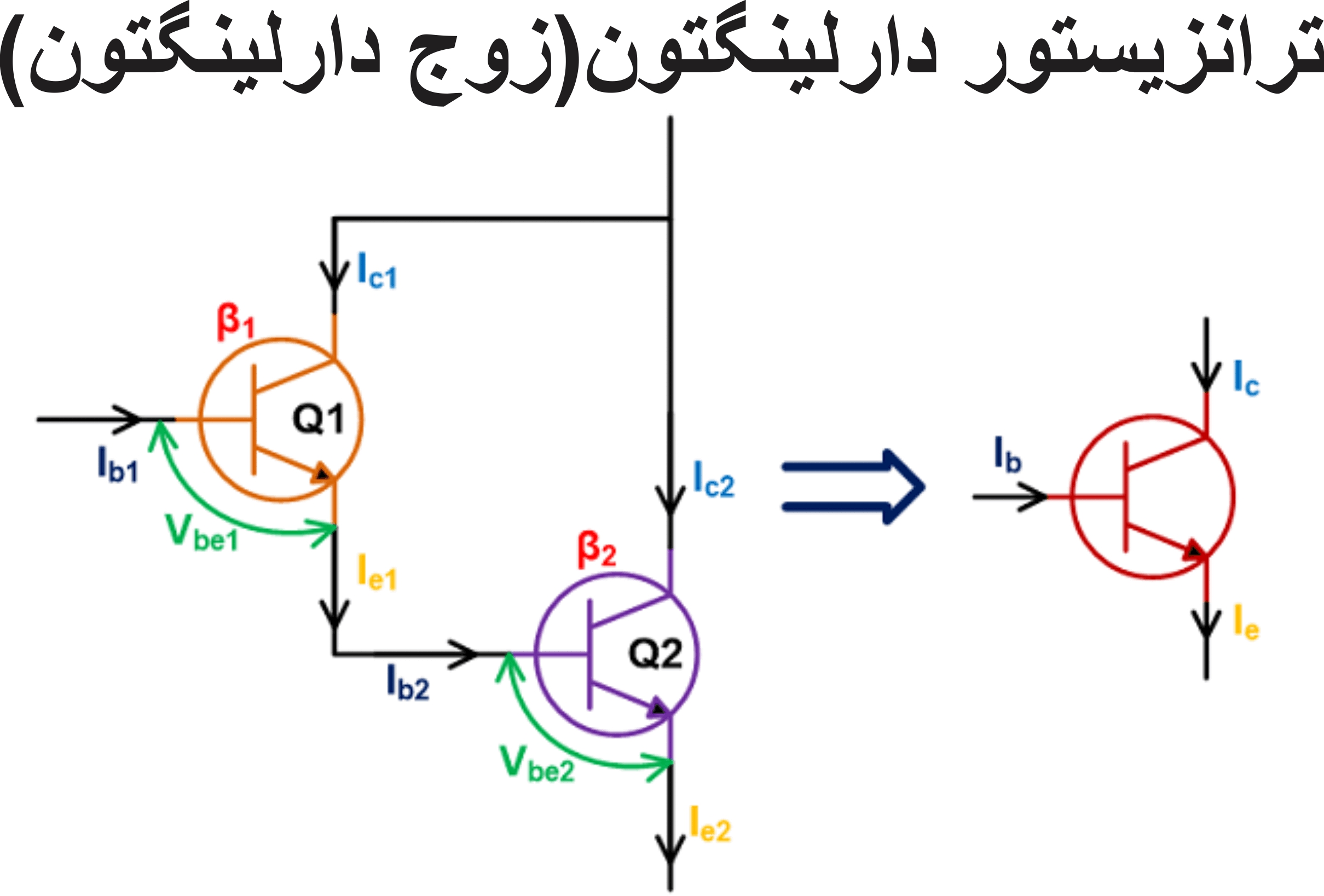
Note: The Darlington transistor configuration and structure in two bipolar transistors increases the switching current for a given base current. These types of transistors do not work well at voltages below 3 volts, but for voltages above 3 volts they turn on completely and go into saturation with very little current. These transistors are often used for switching (turning on and off).
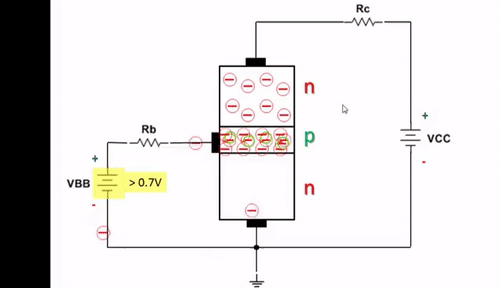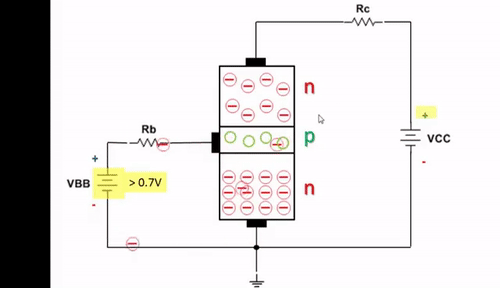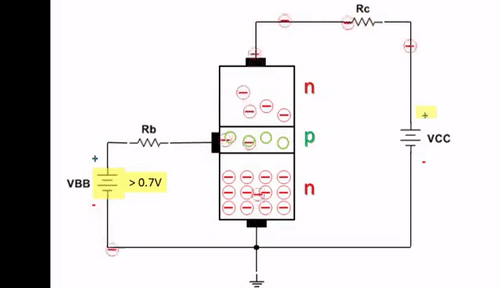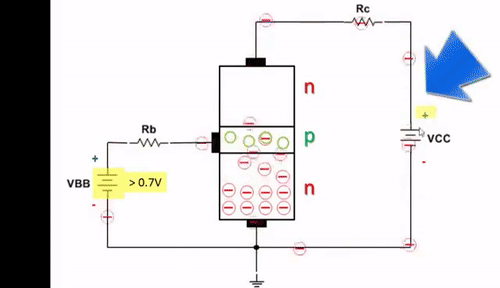
A Darlington transistor is a special arrangement of two standard NPN or PNP bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) connected together. The emitter of one transistor is connected to the base of the other transistor to produce a more sensitive transistor that can handle much higher current, useful in applications where current amplification or switching is required. A Darlington transistor pair can be made from two separate bipolar transistors connected together or a single device made commercially in a single package with standard: base, emitter, and collector connectors and is available in a variety of styles and voltage (and current) ratings. Both NPN and PNP versions of the Darlington transistor are used as amplifiers.
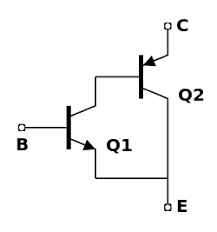
One transistor circuit configuration that can be used to great effect in many cases is the Darlington pair. The Darlington pair offers several advantages. It is primarily used because it offers a particularly high current gain and it also provides a large input to the overall Darlington circuit compared to a single transistor. However, the Darlington pair has some drawbacks.
The configuration of a Darlington pair circuit is quite well-known. It typically consists of two transistors, although theoretically it could contain more. The emitter of the input transistor is connected directly to the second base. The two collectors are connected together. In this way, the base current flows from the first transistor to the base of the second transistor.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized PhD in Nano-Microelectronics