Nanoelectro-lithography and ( thin film deposition techniques) PhD in nano-microelectronics
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
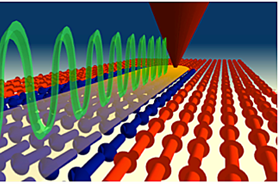
Note: Top-down approaches are used using thin film deposition techniques (spraying, molecular beam epitaxy, pulsed laser deposition, chemical vapor deposition, thermal evaporation, wide electrode, etc.) and nano-lithographic techniques.
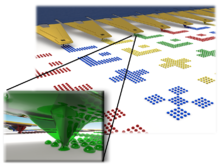
Two approaches are usually followed. In the first method, a thin film (or multilayer film) is grown on a substrate, with precise control of the layer thickness. Depending on the homogeneity of the growing method and the growing equipment used, this area of the substrate can reach large values in the range of tens of centimeters, or beyond. In the second stage, a lithography method for modeling film lateral dimensions micrometer or nanometer used and materials in specific locations delete, In the second approach, the nano-lithography, first on the bed naked is done, after which growth Material increases. This is the so-called lifting technique . A combination of both approaches is often required in multi-step processes to build complex devices.
Integrated optical devices and sub-assemblies based on nano-optical elements realize various advantages. Compared to conventional bulk optics, their size and optical properties make the alignment in the assembly more generous, less carter and less expensive. When combined physically with other nano-optics or other materials in production to create a seamless integrated optics, this eliminates the complications and laminating costs of multiple devices while increasing reliability. Also, array nano-devices can be used in multi-beam or multi-path optical circuits, eliminating the need for separate discrete optics alignment. In general, the manufacturing process of nano-optical elements is flexible and robust, which saves on the cost of the manufacturing process in creating composite and integrated optics. Again, the resulting light is often smaller, stronger, more practical, and easier to collect. Because nano-optical devices are manufactured using wafer-based processes in semiconductor fabrication, this provides flexible sharing capacity in production capacity and supports high-volume production capacity. Slowly
Conclusion :
Top-down approaches are used using thin film deposition techniques (spraying, molecular beam epitaxy, pulsed laser deposition, chemical vapor deposition, thermal evaporation, wide electrode, etc.) and nano-lithographic techniques.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
PhD in Nano-Microelectronics