Section _ reproduction and production of nanowires
Nanowires are quasi-dielectric nanostructures.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
_opt5.gif)
Note: Nanowires are quasi-dielectronic nanostructures with high aspect ratio and large area, where radial strain uniformity allows for unusable combinations of semiconductor materials. It enables countless applications of nanowires in electronics, optics and quantum technologies in general.
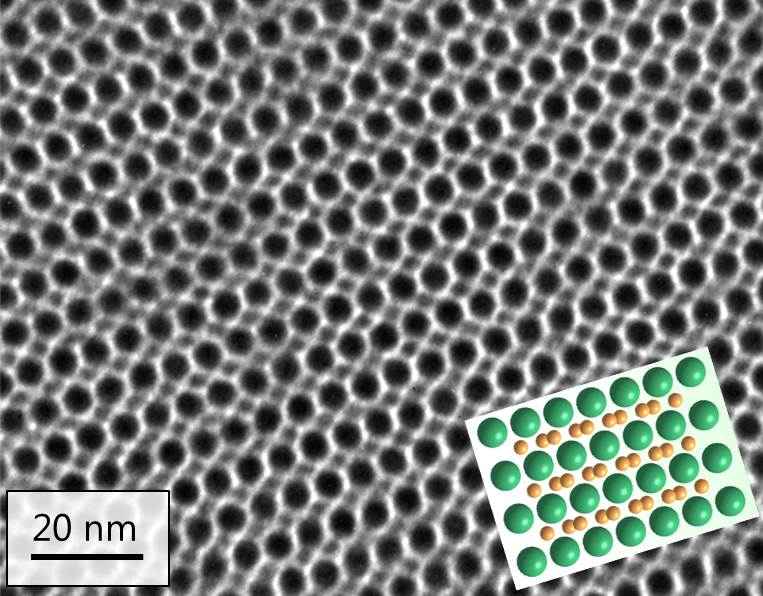
In the multiplication of nanowire particles, they are synthesized in air by calculating the nanowire particles embedded in the alumina pattern. The morphology and phases of nanowires/nanotubes are investigated by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD), respectively. Electron reaction of nanowire particles between oxidation plays a role in the formation of such Nanowire nanostructures.
In the immersion method, the nanowires have enough time to transfer from the particles of the nanowires to the holes; The step of forming uniform nanoparticles is done slowly and finally uniform nanowires are formed. Structural investigation by the multiplication of nanowire particles in the immersion method of uniform nanowires in all pores and in a wide area in the nanowire particles.
By changing the Sr/Fe ratio, there is no change in the morphology of the nanowires. and the spectroscopy of nanowires with different Sr/Fe ratios inside the internal nanoparticles (uniform nanowires), the presence of Fe and Sr elements is caused by strontium ferrite, in the spectroscopy of uniform nanowires, it is observed that the ratio of Sr/Fe nanoparticles to the amount Its stoichiometry in the electromagnetic composition of nanoparticles is closer, while due to the lower solubility of strontium uniform nanowire nanomolecules compared to iron nitrate and the presence of less strontium ions in the reaction with the electromagnetic particles of nanowires, There is a higher amount of Fe ion in the final structure.
Conclusion:
Nanowires are quasi-dielectronic nanostructures with high aspect ratio and large area, where radial strain uniformity allows for unusable combinations of semiconductor materials. It enables countless applications of nanowires in electronics, optics and quantum technologies in general.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics