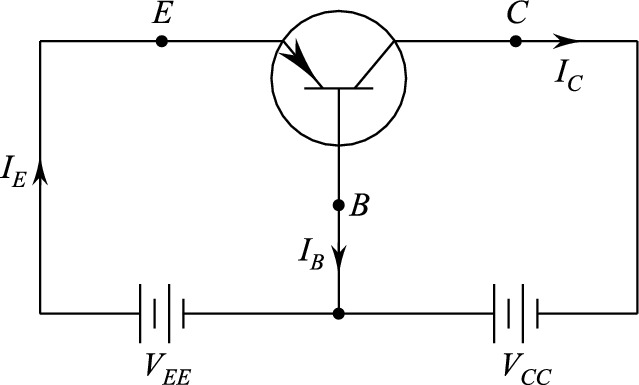
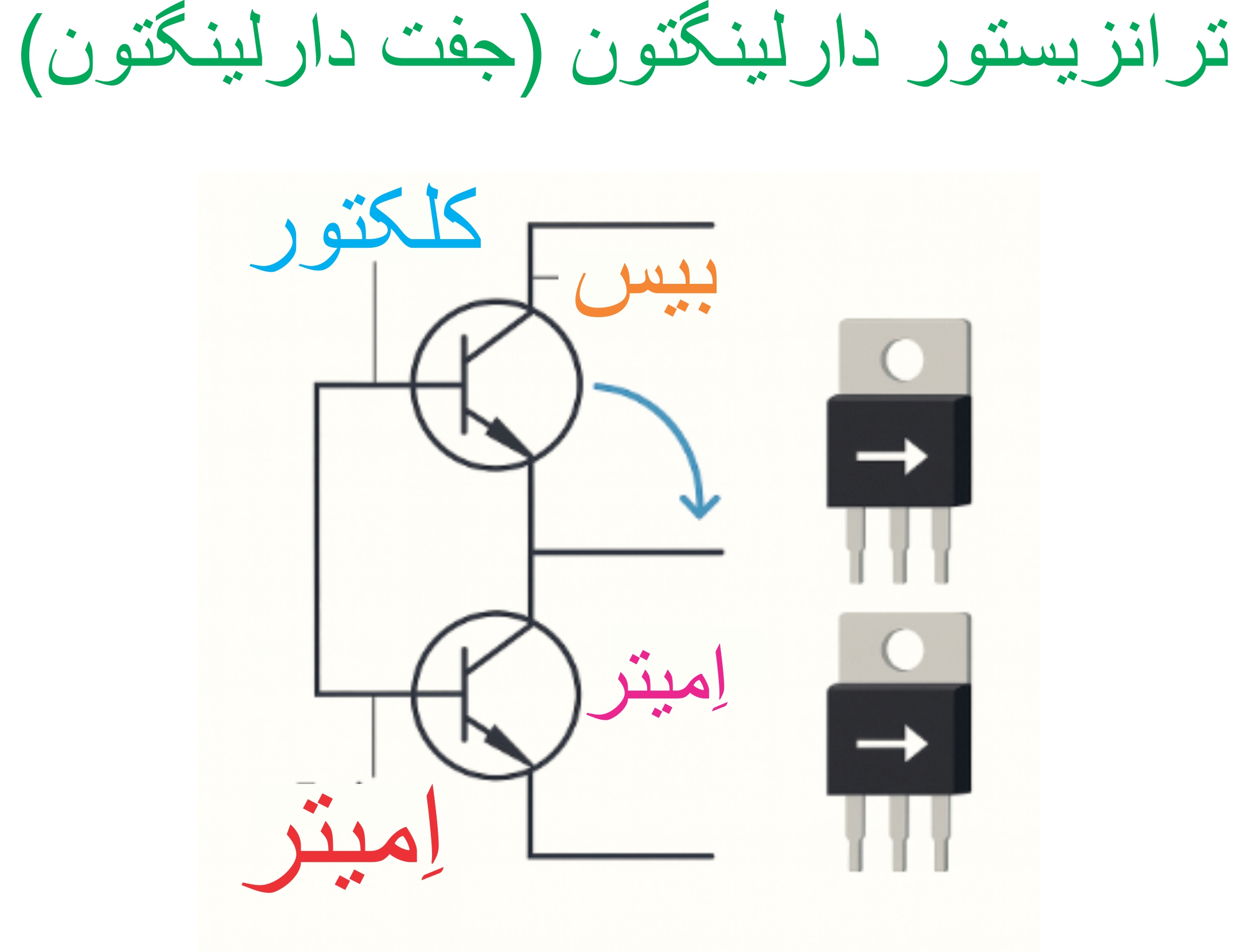
Section _ Understanding (Darlington transistor ) or Darlington pair
Checking (Peak Pulse Emitter Current) in Darlington Transistor Darlington = Pair or Pair
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Darlington transistor specifications include the intrinsic performance index ratio (maximum and minimum), RMS power dissipation, RMS emitter current, peak emitter pulse current, base-to-base voltage, emitter reverse voltage, and operating and storage junction temperatures. RMS stands for root mean square.
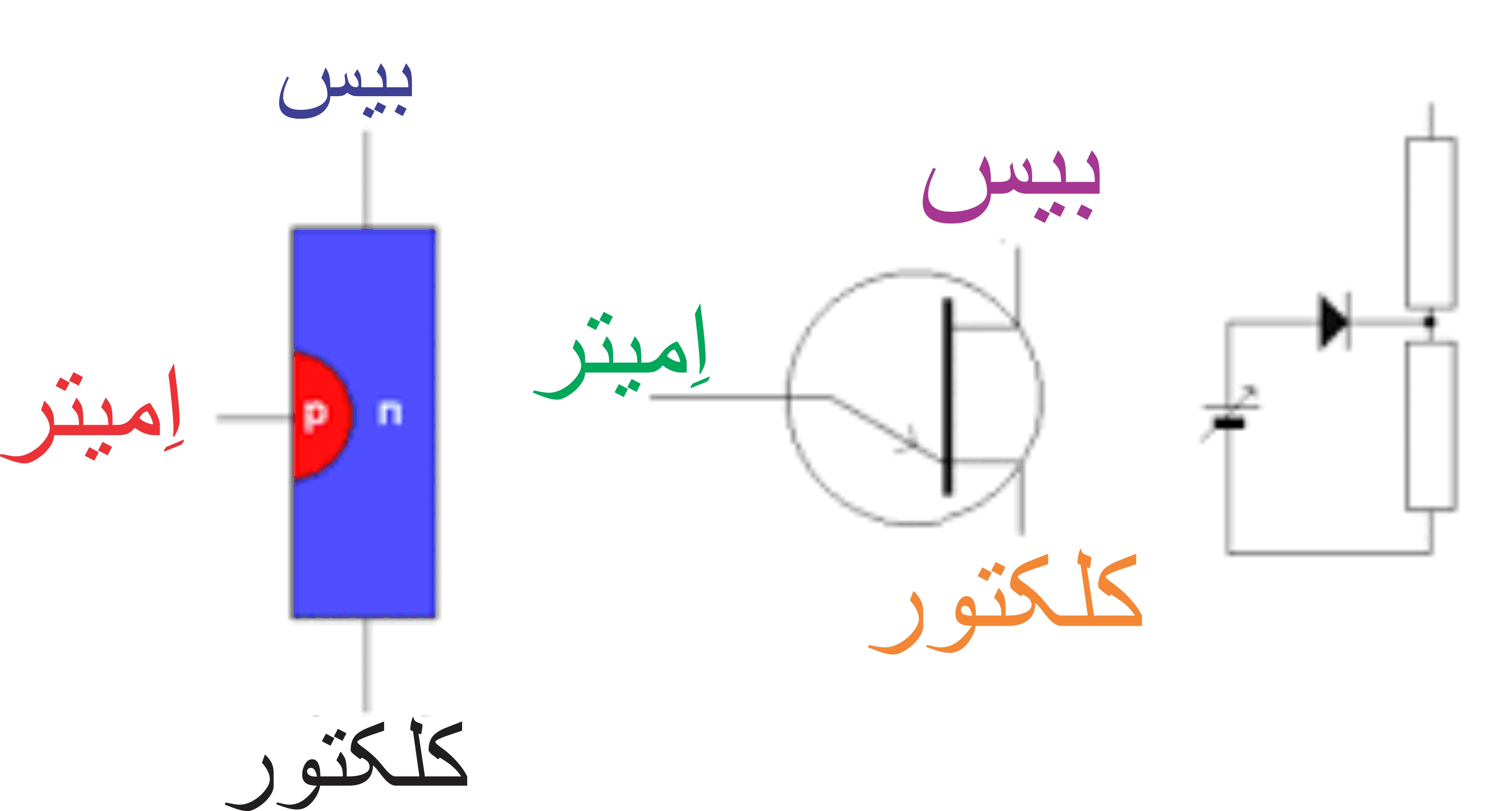
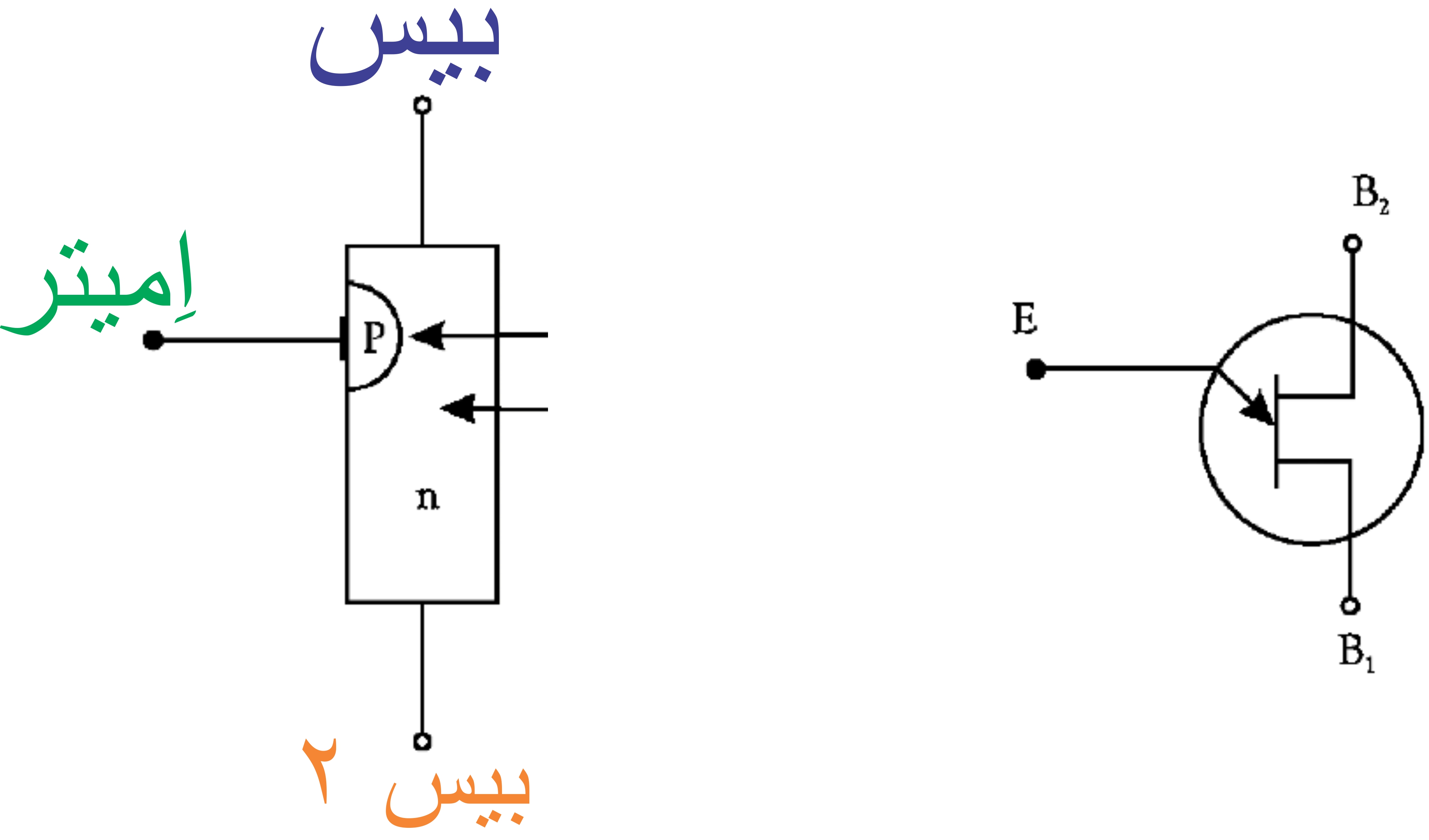
Darlington transistors are three-terminal devices with only one PN junction. When an aluminum tip is connected to one side of an N-doped silicon rod or block, the junction becomes a P-region or emitter. The other two junctions are called base 1 and base 2. With the emitter grounded, the Darlington transistor is reverse biased and no current flows between base 1 and base 2. As the bias voltage at the emitter increases, current flows until the bias voltage reaches a threshold or peak voltage, at which point the emitter to base 2 current increases rapidly (negative resistance). When Darlington transistors are used with an RC timer circuit, they can operate at frequencies up to 1 MHz.
A Darlington transistor can be used to trigger a silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) after a predetermined period of time. Darlington transistors can be the active component in relaxation oscillators. A relaxation oscillator charges a capacitor gradually. At a predetermined voltage, the capacitor discharges rapidly, producing a sawtooth wave. With two terminals, a Darlington transistor is sometimes called a two-terminal diode. An integrated circuit can consist not only of an integrated circuit chip, but also of a transistor circuit such as a single-junction transistor.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized PhD in Nano-Microelectronics



_uay6.gif)