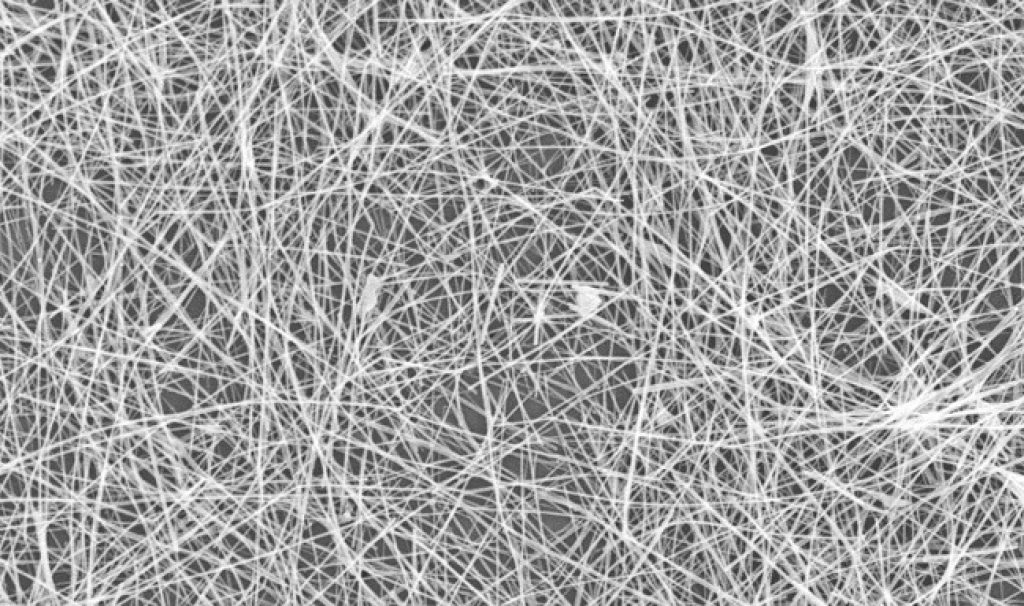
- Oligophenylene vanillin nano wires section
Oligophenylene vanillin nanowires are less than 100 nm in diameter and can be as small as 3 nm.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Note: Oligophenylene vanillin nanowires are less than 100 nm in diameter and can be as small as 3 nm. Typically, nanowires are more than 1000 times larger than their diameter. This huge difference in length-to-diameter ratio compared to nanowires is often referred to as 1D materials. This leads to unique properties not seen in bulk materials, the minute size of nanowires means that quantum mechanical effects become important.
Oligophenylene vanillin nanowires exploit quantum mechanics to produce wires with a wide range of unique nanoelectrical properties. These properties include quantum tunneling, which allows wires made of carbon nanotubes to have very high conductivity with electrons passing through the wire in a ballistic manner. Nanowires have a structure that has an amazing length-to-width ratio . Oligophenylene vanillin nanowires are very thin - it is possible to create nanowires with a diameter of only one nanometer, nanowires are used to create the smallest transistor (nanotransistors). Nanowires "Oligophenylene vanillin" Oligophenylene vanillin can have the properties of insulator, semiconductor or metal. Insulators do not carry electrical charges, while metals carry very good electrical charges. Semiconductors lie between the two and are charged under the right conditions. By placing semiconductor wires in the right configuration, transistors can be made that either act as switches or amplifiers . Some of the interesting and anti-flexible properties of nanowires are due to their small scale.
Some nanowires are ballistic conductors . In normal conductors, electrons collide with atoms in the conductor material. This causes the electrons to slow down as they travel, creating heat as a byproduct. In ballistic conductors, electrons can pass through the conductor without collision. Oligophenylene vanillin nanowires can conduct electricity effectively without generating extreme heat. As the bulk volume is reduced to the size of the nanoparticle, its melting point is lowered, because when you reduce any particle to the nanoscale, there is a significant increase in the surface-to-volume ratio. In the manufacture and propagation of nanowires, a top-down approach and Bottom - up approach . A top-down approach literally means you take a large amount of the material you want to use for the nanowires and etch until you get the right size. A bottom-up approach is an assembly process in which smaller particles join together to form a larger structure.
Note: Oligophenylene vanillin nanowires are less than 100 nm in diameter and can be as small as 3 nm. Typically, nanowires are more than 1000 times larger than their diameter. This huge difference in length-to-diameter ratio compared to nanowires is often referred to as 1D materials. This leads to unique properties not seen in bulk materials, the minute size of nanowires means that quantum mechanical effects become important.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics