Electrical properties of single layer nanotubes (CNT) and electrical conductivity of CNT nanotubes (based on micro-nano-electronics) (PhD-Research)
Researcher and author: PhD student Afshin Rashid
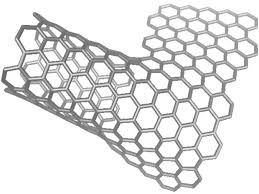
Note: Single-walled carbon nanotubes or CNTs can be very good conductors or semiconductors. This high electrical conductivity depends on the precise geometry of the carbon atoms. Single-walled carbon nanotubes, or CNTs, are referred to as one-dimensional phenomena.
The reason for the interest in these single-walled CNTs (CNTs) and their attempt to replace them in the industry is due to their excellent mechanical properties and electrical conductivity, such as metals. It is difficult to stabilize their properties during the processing of nanotube polymer. However, nanotubes produced using a technique involving horizontal and vertical motions are structurally controllable in addition to being held constant.
One of the disadvantages of multi-walled nano-tubes compared to single-walled ones is that they are less robust because the interlayer connections are weak. However, since the current applications of CNT monolayers in reinforcing electric current transmission devices are improving the thermal and electrical properties, there is much to improve the mechanical properties and application of multi-walled carbon nanotubes or CNTs. On the one hand, the techniques available to produce single-walled nanotubes are not efficient enough and do not provide the required purity. The purification of these materials is very difficult and may eventually damage the CNT's single conductive electronic nanotube structure.
Conductive and semiconducting state of CNT monolayer carbon tubes based on geometric structure
CNT carbon nanotubes are conductive or semiconductor based on their geometric shape and monolayer carbon nanotubes depending on how their constituent graphite plates roll . In other words, because the nanotubes at the molecular level look like a wired beam, interconnected by carbon atoms , they form hexagonal walls that are only a few nanometers in size. . The torsion angle of a nanotube, defined as the angle between its hexagonal pattern axis and the tube axis, determines the conductivity or non-conductivity. The radius change also allows for bond lengths to be insulated and metal nanotubes insulated. So we can say that there are two basic parameters that play a key role , one is the structure of the nanotube and the other is its diameter and size.
Conclusion :,
In electrical conduction from a conductor to a semiconductor or a switchable electrical insulation of nanotubes depends on their molecular structure and chiral angle . Since carbon nanotubes are capable of passing electrical current by frictionless ballistic electron transfer - 100 times more current than passing through copper wire - so nanotubes are an ideal choice for many micro applications Are electronics.
Author: Engineer Afshin Rashid
PhD student of Nano-Microelectronics at Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch, Tehran