Graphene based nanotransistors Nano graphen transistor (PhD in nano-microelectronics)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Note: Graphene nanomaterial, which is a honeycomb structure and as thick as a carbon layer, due to its properties such as high mobility of electrons and holes and thermal and mechanical stability, used in the nanoelectronics industry and the manufacture of graphene nanotransistors. FET was placed.
Although graphene is a semiconductor material with zero gap and unsuitable for logic circuits, it uses nanoelectronics technology to create different forms of this material to produce FET graphene nanotransistors with different gaps (eV 2.1-0). Graphene nano-strips, multilayer graphenes and graphene grown on SiC to amplify FET graphene nanotransistors are such shapes that have had a tremendous impact on the design industry of new nanoelectronic devices. FET graphene tunnel field in which in the drain and source areas of graphene without energy band gap and in its catalytic part of graphene with limited band gap (eV2 / 1) has been used.
In the proposed structure, the rate reaches a suitable level, which is a FET graphene nanotransistor, which is a suitable value for digital structures, and also the output properties show a very good state of saturation. There are basic parameters such as doping concentration, drain voltage, dielectric thickness and the difference between the working functions of the gate and graphene electrodes in the three structures. Increasing the doping rate has an effect on the on current and increases it, which increases the doping rate of FET graphene nanotransistors, which make these structures very suitable for use in low power devices.
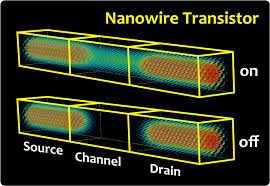
The term transistor is a combination of the words transfer and resistance. In a FET graphene nanotransistor, the resistance between two electrodes can be transmitted or controlled by a third electrode. Source connection and drain connection take place through a semiconductor (graphene nanoplayer). The nano electrode of the gate is separated from the semiconductor by the electrical insulation of the dielectric layer of the gate. Therefore, the gate nano-electrode is attached to the semiconductor in the form of a graphene layer and controls the electrostatic potential of the semiconductor / insulation interface .
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
PhD in Nano-Microelectronics