Investigation of the structure of graphene in CNTs multilayer carbon nanotubes (based on nano-micro-electronics PHD) Educational-research doctorate
Researcher and author PhD student : Afshin Rashid
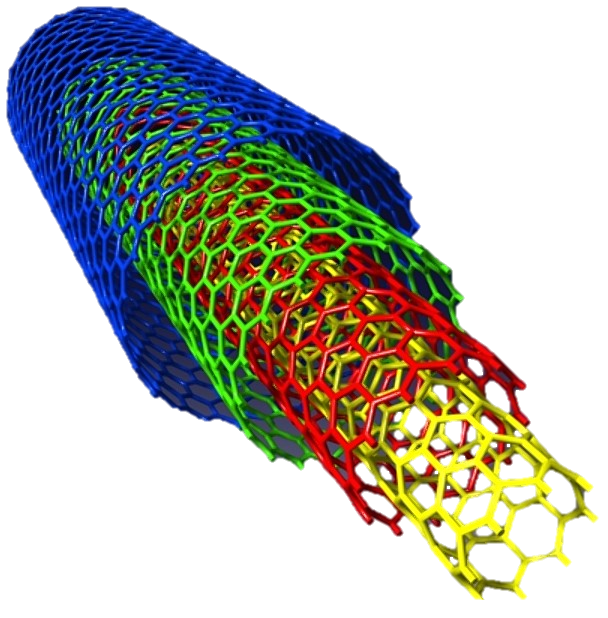
Note: Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are a carbon electrode. They are formed in the form of cylindrical carbon molecules and have new properties that make them useful in a wide range of nano-microelectronic applications.
They show extraordinary power and unique electrical properties and are efficient conductors of heat. Mineral nanotubes have also been synthesized. Nanotubes are members of the structural family of fullerenes, which include buckyballs, while spherical buckyballs They are a cylindrical nanotube and at least one end of it is normally covered with a hemisphere of buckyball structure. Their names are taken from their size. Graphene has outstanding nanoelectronic properties, very high electron mobility and unparalleled nanoscale guidance. It is an excellent conductor that transmits electrons at a rate ten times faster than silicon. This feature makes Hagrafen an ideal candidate for future generations of nanotechnology applications such as nanoparticles, nanotubes, supercapacitors and nanosensors.The effects of uneven edges as a problem in the construction of CNTs multi-walled nanotubes and in graphene nanofibers with uniform, low width (GNRs) and controllable edges, cover this defect.
Graphene nanofibers inside CNTs or multilayer nanotubes are an extremely good electrical conductor and a semiconductor that can be used in integrated circuits (ICs), small chips with millions of transistors . Increasing the length of the graphene strip at low voltages reduces the electric current in the nanotubes and eventually creates a gap in the conduction curve. The reduction in electrical conductivity can be due to the effects of quantum interference, and the structure-governing conductivity in the presence of a gap in conductivity is described based on an intensified tunneling. On the other hand, as the width of the graphene nanotube increases with the connection points in the CNTs nanotubes with the central region, the electron flux pathways to the central region of the CNTs multilayer carbon nanotubes increase and the conductivity increases .Graphene plates, in addition to having many electrical properties, and the conductivity of carbon nanotubes, have unique electrical transport properties, such as the quantum effect of semi-correct semiconductors, minimal conduction, and so on. that compared with carbon nanotubes of greater flexibility Hstnd.haml charge in graphene behave like massless fermions show day. The above features have made graphene a suitable candidate in nanotechnology structures.
Conclusion:
At a certain range of electron energy, the electron waves interfere with each other and the electric current is weakened. Therefore, by increasing the length of the GNR graphene nanofibers, a gap is created in the convection curve of the GNR graphene strips inside the CNTs multilayer carbon nanotubes.
Author: PhD Student ( Afshin Rashid)