🔬 بخش نانو سنسور های بیولوژیکی _ الکتریکی
بررسی نانو سنسور های بیولوژیکی _ الکتریکی (Nano bio sensor) مانند حواس بویایی و چشایی که به شناسایی بوها و طعم های مختلف
پژوهشگر و نویسنده: دکتر ( افشین رشید )
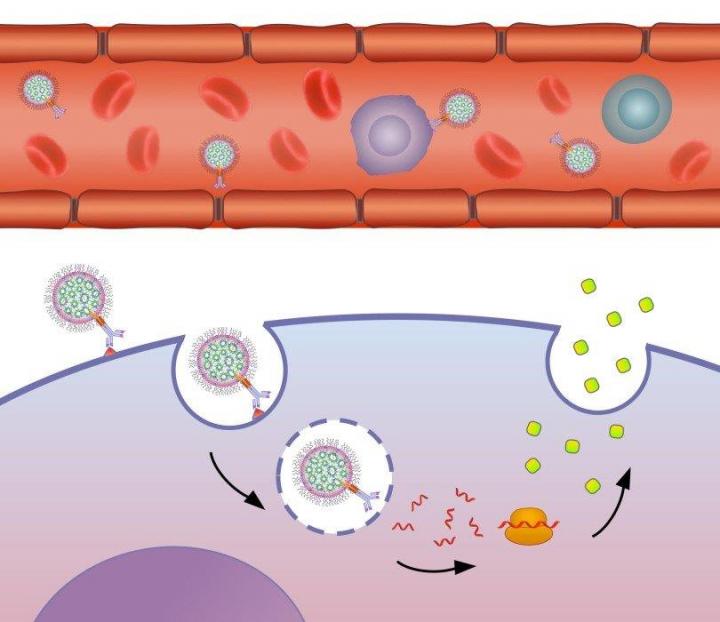
نکته: حسگر های زیستی طی سالهای اخیر مورد توجه بسیاری از مراکز تحقیقاتی قرار گرفته اند. از آنجا که حسگرهای زیستی ابزاری توانمند جهت شناسایی مولکولهای زیستی هستند، امروزه از آنها در علوم مختلف پزشکی، صنایع شیمیایی، صنایع غذایی، مانیتورینگ محیط زیست، تولید محصولات دارویی، بهداشتی و غیره بهره میگیرند.
نانو سنسور های بیولوژیکی (Nano bio sensor) حواس بویایی و چشایی انسان که به شناسایی بوها و طعم های مختلف میپردازد و یا سیستم ایمنی بدن که میلیونها نوع مولکول مختلف را شناسایی میکند، نمونه هایی از حسگرهای زیستی طبیعی هستند. بیشترین کاربرد حسگرهای زیستی در تشخیصهای پزشکی و علوم آزمایشگاهی است، در حال حاضر بیوسنسورهای گلوکز از موفقترین بیوسنسورهای موجود در بازار بوده که برای اندازهگیری غلظت گلوکز خون بیماران دیابتی استفاده میشود. در پانکراس بیماران دیابتی به میزان کافی انسولین تولید نمیشود. در این گونه موارد برای تنظیم مصرف میشود. انسولین، سنجش مداوم میزان گلوکز خون ضروری است. حسگرها به بیماران مبتال به دیابت کمک میکند تا در طول روز به سنجش سطح گلوکز خون خود پرداخته و در زمانهای مورد نیاز انسولین تزریق کنند.نانو سنسور های بیولوژیکی (Nano bio sensor) ، نام گروهی از حسگرها است. این حسگرها به گونه ای طراحی میشوند تا تنها با یک ماده ی خاص واکنش نشان دهند. نتیجه ی این واکنش به صورتِ پیامهایی در میآید که یک ریزپردازنده، میتواند آنها را تحلیل کند.
کاربردهای مختلفی برای نانو سنسور های بیولوژیکی _ الکتریکی (Nano bio sensor که در ذیل اشاره میشود:
- تشخیص و درمان بیماریها )سرطان، دیابت و...(
- تشخیص بیماریها در سطح ژن)سرطان، دیابت و...(
- تشخیص عوامل بیماریزا
- اندازهگیری داروها و متابولیتهای آنها، کشف داروهای جدید و ارزیابی فعالیت آنها
- ارزیابی و اندازه گیری آنالیتهای موجود در نمونه بیولوژیک
- تشخیص سریع بیماریها با استفاده از تستهای سریع یاcare- of-Point ، ویژگی این تستها سرعت و ارزان بودن روش آزمایش است.
نتیجه گیری :
نانو سنسور های بیولوژیکی (Nano bio sensor) ، نام گروهی از حسگرها است. این حسگرها به گونه ای طراحی میشوند تا تنها با یک ماده ی خاص واکنش نشان دهند. نتیجه ی این واکنش به صورتِ پیامهایی در میآید که یک ریزپردازنده، میتواند آنها را تحلیل کند.
پژوهشگر و نویسنده: دکتر ( افشین رشید)
دکترایِ تخصصی نانو _ میکرو الکترونیک