Carbon nanotubes reduce toxicity and damage to the cells of living organisms (PhD in nano-microelectronics)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
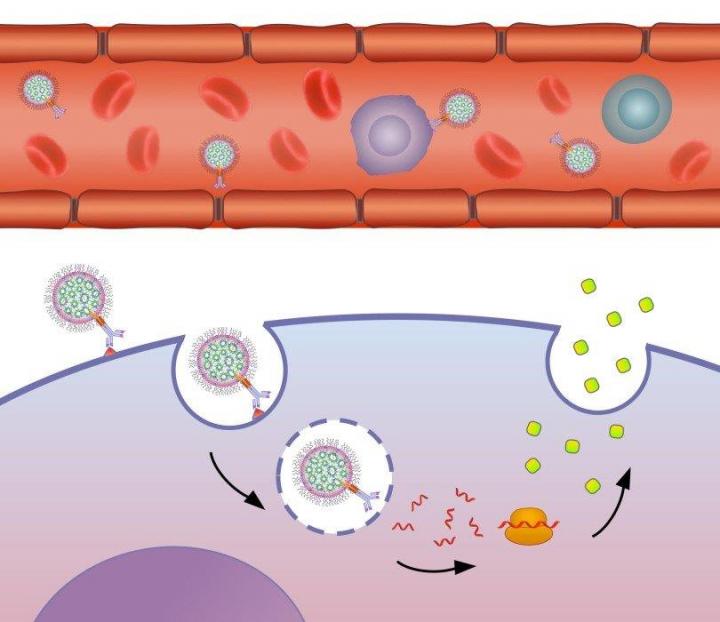
Note: Carbon nanotubes reduce toxicity and damage to living cells. Biocompatibility of carbon nanotubes makes it possible to take advantage of their unique properties in the biological environment. Connecting factor groups can be on external surfaces, through points that have structural defects.
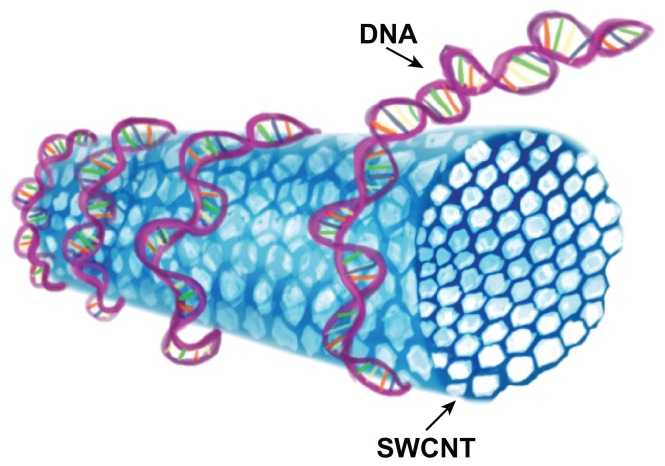
In the structure at the two open ends of nanotubes and even by inserting molecular structures into the interior of the nanotube can be done. While there are many ways to functionalize nanotubes, one of the common methods of coating nanotubes with polyethylene glycol ( PEG) is widely used. Polyethylene glycol polymer coating is biocompatible. It is mostly used in nano-biosensors and by improving the behavior during bonding, these materials can be coated by covalent or non-covalent CNT bonding. With the covalent bonding of PEG to the CNT surface, the molecular weight increases.Attempts have been made to increase their solubility and biocompatibility by modifying the molecular modification in the surface properties of layered carbon nanotubes by bonding phospholipid-polyethylene glycol PEG derivatives on the nanotube surface.
Methodology of cellular nanostructures (nanocarbon CNT tubular tubes
Use of Phospholipid-Polyethylene Glycol in the Solubilization of Carbon Nanotubes To functionalize CNT carbon nanotubes, phospholipid-polyethylene glycol derivatives can be used with different chain lengths and branched or linear structures. The presence of nano-functional groups such as nanoamines at the end of the polyethylene glycol chain also allows the loading of biological nanomolecules and thus the use of nanotubes in nanosensors and biosensors.
Conclusion :
The results of this paper confirm that the modification of the structure of electrons and chemical surfaces in nanoparticles can increase their cellular structure by maintaining their function, especially in the group of nanosensors and biosensors.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
PhD in Nano-Microelectronics