_ Department of Integrated Circuits (ASIC)
ASIC type integrated circuits ( completely customized design )
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
_1j85.jpg)
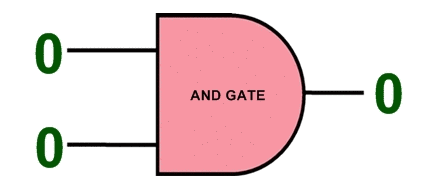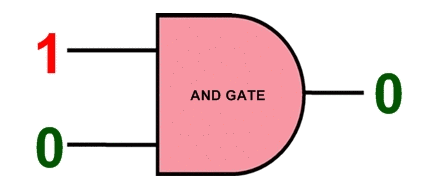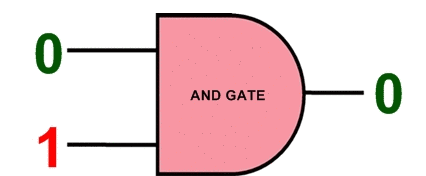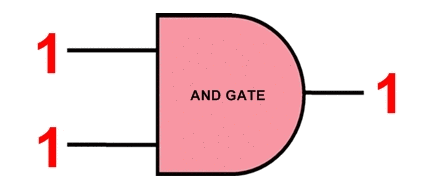
ASIC Integrated Circuits ( Completely Custom Design ) This type of ASIC is the most flexible because it includes ASIC design down to the transistor level. The ASIC design can be adjusted to the exact requirements of the circuit. While it offers the highest degree of flexibility, the costs are much higher and it takes more time to develop. The risks are also higher because the whole design is untested and not built from stronger elements that have been used before.
In a broad sense, an application-specific integrated circuit or simply an ASIC can be defined as an integrated circuit that is customized for a specific application or end use, rather than being used for general purposes. ASICs are quite different from other standard ICs such as microprocessors or memories because they are designed for use in a wide variety of applications. In contrast, an ASIC can only be used in the application it is specifically designed to run.
Due to the custom application-specific nature of ASICs, they often have higher performance while being small in size, consuming less power and dissipating less heat compared to a standard IC solution. Another major difference between standard ICs like memories, for example, and ASICs is that the ASIC designer can be directly from the customer, who may have a clearer idea of the application. The history of ASIC designs and technology can be characterized by the continuous growth and evolution of different ASIC design styles. Statistically, CMOS-based gate array style ASICs are the dominant type, but there are several other types of ASIC designs.
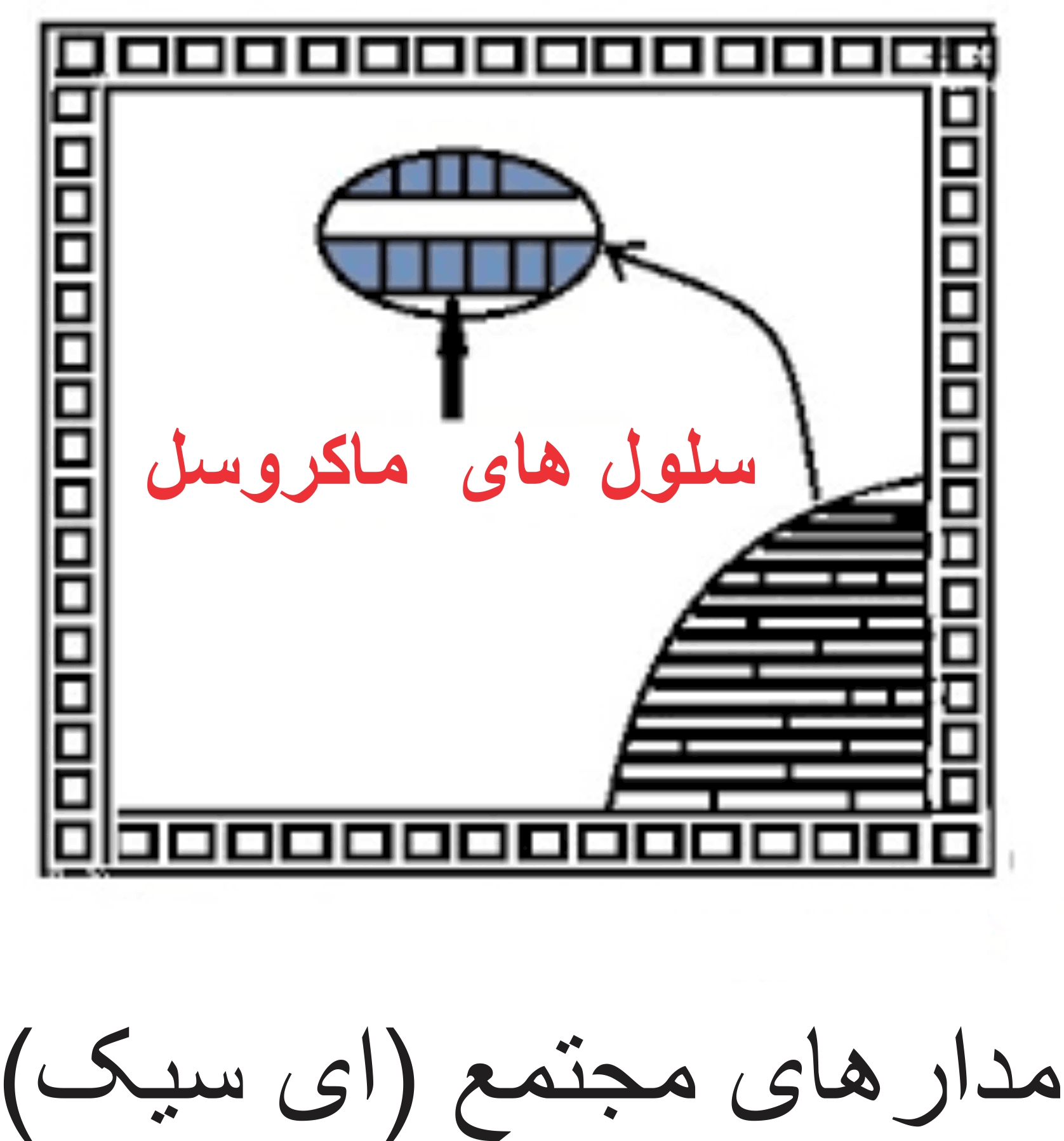
Semi-custom ASICs are further divided into gate array based designs and cell based designs. Gate arrays are further divided into channel and non-channel arrays while cell-based designs are divided into standard cells and macrocells. In a fully custom ASIC, all logic cells, circuits and layouts are designed specifically for that particular ASIC from scratch. A designer may only choose a completely custom ASIC design if he thinks that either the existing libraries are not fast enough, or the logic cells are not small enough, or the power consumption is high. The main advantage of fully custom ASICs over other IC designs is that they provide the highest possible performance in the smallest possible die size. But this high performance and small size comes with increased design time, complex design and overall cost of the IC itself.
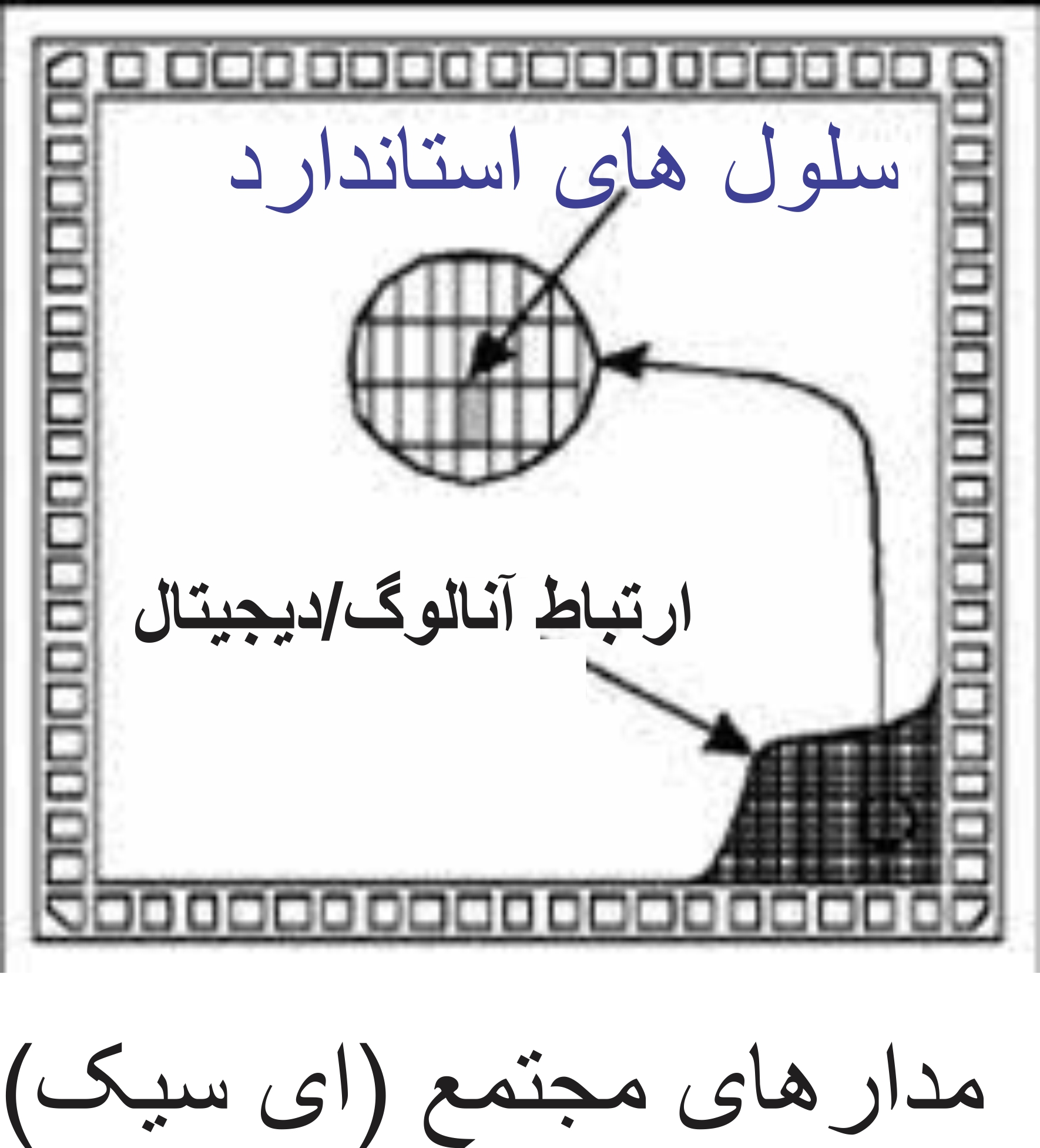
Some of the most common full custom ASISs are microprocessors, memories, analog processors, analog/digital communication devices, sensors, converters, high voltage ICs for automobiles, etc. To shorten the design time and reduce the cost of fully custom ASICs, several other design methods have been developed, which are called semi-custom ASIC designs. Typically, the lowest level of the hierarchy involved in semi-custom design is the logic level or gate level. This is in contrast to fully custom work where individual transistor design and layout may be involved.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics