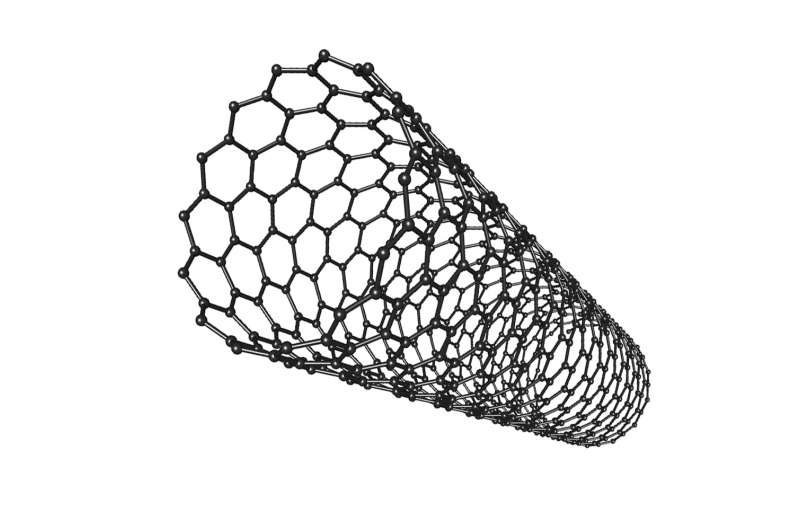
Graphene nanotubes inside multilayer nanotubes CNTs or multilayer nanoparticles (nano-microelectronics)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Note: Graphene nano-strips inside multilayer CNTs or multilayer nanotubes are an extremely good electrical conductor and a semiconductor usable in integrated circuits (ICs), small chips with millions of transistors .
Increasing the length of the graphene nano strip at low voltages reduces the electrical current in the nanotubes and ultimately creates a gap in the conduction curve. The reduction in electrical conductivity can be due to the effects of quantum interference, and the conductivity governing the structure in the presence of a gap in the conduction is described in terms of resonant tunneling. On the other hand, by increasing the width of the graphene nano strip along with increasing the connection points in the CNTs nanotubes with the central region, the electron flow paths to the central region of the multilayer CNTs increase and the conductivity increases .Graphene plates, in addition to having many electrical properties, and the conductivity of carbon nanotubes, have unique electrical conductivity properties such as the correct half-quantum effect, minimum conductivity, etc. The structure is also straight. that compared with carbon nanotubes of greater flexibility Hstnd.haml charge in graphene behave like massless fermions show day. The above properties have led to graphene being considered as a suitable candidate in nanoelectronic structures.
Graphene strips with finite width are known as graphene nano strips, which according to the shape of their edges, they are divided into two types of armature and zigzag. It is possible to make graphene nano strips with different widths. They are metal, while armature graphene nano-strips can exist in both metal and semiconductor forms with a certain energy gap due to the width of the strip. Nano-graphene tape has armature edges that are restricted to these two semi-incomplete metal nano-strips from left and right. In both structures, by increasing the number of single cells in the multilayer nanotubes of CNTs, the electrons adjacent to the equilibrium are reduced and a threshold voltage is created in the current-voltage characteristic curve and in the conduction curve.
Conclusion :
In CNTs carbon nanotubes, the physical origin of such behavior can be due to the interference effects of electron waves on the carbon branches of graphene ribbon. In a certain range of electron energy, electron waves interact destructively and the electric current is attenuated. Therefore, by increasing the length of GNR graphene nanoparticles, a gap appears in the conduction curve of GNR graphene strips inside CNTs multilayer carbon nanotubes.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
PhD in Nano-Microelectronics