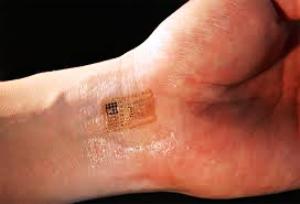
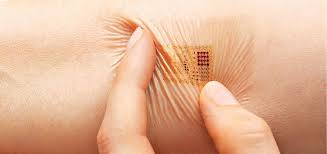
Benefits of nano (bio-sensors) over other physiology measurement systems (based on nano-microelectronics) (Ph.D.)
Researcher and author: Engineer Afshin Rashid
Important Note: Nanoelectronics are crucial in the manufacture of nano-biosensors (physiology and biology), physiology is one of the most important branches of biology that studies the vital functions of living organisms, organs, tissues, cells, and cell elements. In order to gain a deep understanding of vital functions, it is attempted to examine the properties and relationships between these practices and their variations in different environments or in various living conditions using the relationships of physics and mathematics.
Easy to use, often without the need for the specialist, low cost, high sensitivity and accuracy, high selectivity and specificity of operation, no need for advanced equipment, and time and expense to diagnose analytes in small centers and centers with low facilities and even at home. It also applies. Biological elements are the major determinants of biosensor selection, which are mainly divided into four groups, as follows :
Antibodies
2. Enzymes
3. amino acid
4. Cellular structures / cells
Biosensors are divided into two major groups based on how the analyte is identified:
Biosensors based on direct detection of antigen: The acceptor reaction with the analyte is directly detected by the sensor. The biological elements used in this group are cellular receptors and antibodies.
2. Biosensors based on indirect detection of antigen: The acceptor reaction with the analyte is detected indirectly by the sensor. The biological elements used in this group are labeled compounds, such as labeled antibodies or catalytic compounds such as enzymes .
Methods of fixation of biological components:
In order to make a stable biosensor, the biological component must be specifically attached to the transducer, such a process is called stabilization. Five methods are presented for this purpose:
1. Surface adsorption
2
Enclosure
4. Transverse link
5. Covalent link
Manufacture and replication of biosensors (biosensors) in the human body and other organisms for specific cell-environmental measurements
A biosensor is defined as a measurement system comprising a probe with a biologically sensitive material or a biosensor, a physics and chemistry and transducer detection element.
Biosensors are becoming the broadest tool for nano-electronics for physical-environmental applications because biosensors are easy, fast, low-cost, highly sensitive, and highly selective in advancing next-generation drugs such as personalized drugs and identifying super-point of care. . Disease markers in conventional biosensors and biosensing assay techniques and highlighting recent advances are important sensors such as SPR-based biosensors, FET-based biosensors, and AuNPs-based biosensors from a smart biotech perspective .
(Conclusions) on the process of proliferation and growth of biosensors
Electrochemical biosensors are the most widely studied biosensors, manufactured and reproduced because of the advantages of low detection limit, specificity, ease of manufacture and ease of use.Action. Due to recent advances in electronic devices , these biosensors can be used as in-chip laboratory devices for in vivo monitoring or as a handheld device for on-site monitoring.