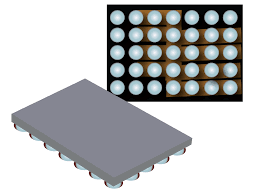
حالت پایه چسبیدن در آیسی ic و چیپ های BGA (پایه توپی) در مدارات الکترونیکی و حالت اتصال کوتاه در بورد الکترونیکی(برق _ الکترونیک)
پژوهشگر و نویسنده: دکتر ( افشین رشید )
نکته : مهمترین عامل پایه چسبیدن در آیسی ic و چیپ های BGA (پایه توپی) در مدارات الکترونیکی و حالت اتصال کوتاه در بورد الکترونیکی میتواند شامل (حرارت و کارکرد زیاد مدار، ضربه ، رطوبت و حالت لحیم سردی) در مدارات الکترونیکی باشد .آیسی ic و چیپ های BGA (پایه توپی) بسیار حساس در برابر عوامل فیزیکی میباشند .
در آیسی ic و چیپ های BGA (پایه توپی) به جای اینکه پایه های آی سی در اطراف آن باشد در زیر آی سی می باشد.در پایه ها از لحیم به صورت توپی استفاده شده است که بعد از مونتاژ این پایه ها به برد لحیم می شوند.
این مدل چیپ یه نوع از ic های SMD میباشد. که توی خیلی از وسایل الکترونیکی مثل موبایل و تجهیزات مخابراتی، مادر برد کامپیوتر و خیلی موارد دیگر در بورد های الکترونیکی استفاده میشود.چون این ای سی چیزی تحت عنوان پایه ندارد و یعنی مثل ای سی های DIP یا SMD های دیگه پایه ی سخت ندارد و جنس پایه های اون از قلع میباشد و این پایه ها دقیقا در کف ای سی قرار گرفته است ؛ برای تعویض ما به دستگاه هیتر نیاز داریم؛ برای این کار از هیتر بادی استفاده میکنیم اما برای چیپ های حساس مثل مادر برد میشه از هیتر مادون قرمز استفاده کرد.
چیپ های BGA مزایای بسیاری دارد و در نتیجه به طور فزاینده در ساخت مدار های الکتریکی مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد.آرایه شبکه توپی ، به دلیل نیاز به داشتن بسته قوی تر و مناسب تر برای ساخت مدار های مجتمع با تعداد زیاد پین ، بسته BGA ساخته شد. با افزایش سطوح ادغام، برخی مدارهای مجتمع بالغ بر 100 پین دارند.
نویسنده: دکتر (افشین رشید )