Common technologies of nanoelectronics in (quantum nano-memories)
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
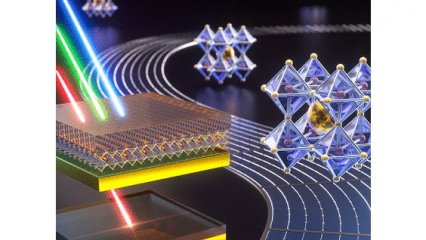
Note: Common nanoelectronics technologies in nanomemories hardly meet the demands, but nanotechnology offers better solutions. One of the new information storage tools is the use of nickel quantum dots in nanometer sizes, which are expected to be used to store terabytes of data, even in homes and in personal use.
Given the relatively large (physically speaking) storage devices we have now and the fact that we need gigabyte sizes in various areas, there is a huge potential for activity in this area.Each quantum dot consists of a single ball of several hundred atoms that can have one of two magnetic states. This allows them to contain a single bit of information (zero or one), as is customary in machine computing. In conventional hard disks, the data bits must be spaced far enough apart to avoid reciprocation. Quantum dots act as completely independent units that are not structurally connected, so they can become somewhat closer to each other. They can be arranged to a certain density that allows any type of information to be stored up to 5 terabytes in a space the size of a postage stamp. Activities should continue until these nanodots work better and work with other computing devices such as silicon chips.
The science and technology of nanoelectronics provide different possibilities of nano molecular memory . For example, photorefractory materials represent only one type of optical memory. In fact, by using nano technology, the storage capacity of information can be increased by a thousand times or more. Storing subject information is very important and necessary, which can be done in different ways through nanomolecular memories . One of the new information storage tools is the use of nickel quantum dots in nanometer sizes, which are expected to be used to store terabytes of data. According to nano molecular memories, there is a high potential for activity in this field.Each quantum dot consists of a single ball of several hundred atoms that can have one of two magnetic states. This allows them to contain a single bit of information (zero or one), as is customary in machine computing. In conventional hard disks, the data bits must be spaced far enough apart to avoid reciprocation. Quantum dots act as completely independent units that are not structurally connected, so they can become somewhat closer to each other.
Conclusion:
Current nanoelectronics technologies in nanomemories hardly meet the demands, but nanotechnology offers better solutions. One of the new information storage tools is the use of nickel quantum dots in nanometer sizes, which are expected to be used to store terabytes of data, even in homes and in personal use.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics