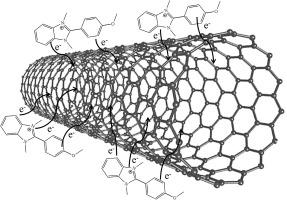
_Part of the process (discharging) for electric nanotubes
Additional ability to store energy in nanotubes several times the volume of graphite electrodes
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Note: In nanotubes, every three carbon atoms have the ability to store one lithium ion, while in graphite, all six carbon atoms have the ability to store one lithium ion. Also, the ability to store energy in nanotubes is several times the volume of graphite electrodes.
A lot of hydrogen can be stored in nanotubes for energy and fuel cell applications. have become superconductive. The radius of these superconducting nanotubes is only 6.4 nm. Phase transition in one or two dimensional systems where room temperature superconductivity can be found in carbon nanotubes and graphene particles and room temperature superconductivity in them. When the liquid passes through coils of single-walled carbon nanotubes, an electric voltage is generated. This technique is used to make liquid flow sensors to detect very small amounts of liquids and also to generate voltage in biomedical applications.
Also, liquids with high ionic strength produce more voltage . The increase in thermal power and resistance of nanotubes is proportional to the third root of the mass of atoms and molecules. Also, heating increases the strength of the nanotube and increases its tensile strength by six times, and its conductivity also increases. Due to the collision of atoms or molecules with the carbon nanotube, its electrical resistance changes.
Electric arc discharge method
In this method, carbon atoms are heated and vaporized by high current passing through the anode and cathode inside the helium gas plasma . The electric arc method is the most common and perhaps the simplest method for the production of carbon nanotubes, and in it a mixture of nanotubes and impurities is produced, which is able to separate the nanotubes from carbon black and metals . Talisauri in the raw product is essential. In this method, nanotubes are produced through the electric arc evaporation of two carbon rods that are opposite each other and approximately 1 mm apart. The electrodes are placed in a chamber filled with an inert gas (helium or argon) at a relatively low pressure of 56-766 mbar. Creating a potential of about 26 volts with a current in the range of 56-166 amperes causes an electric discharge in the gas at a high temperature, and the heat caused by the discharge evaporates one of the carbon electrodes and a deposit in the form of small rods is obtained on the other electrode. to be
Conclusion :
The ability of electronic storage (superconductivity) in carbon nanotubes and graphene particles has made nanotubes an ideal choice for many applications . The manufacturing of tools is concentrated, and they will have the possibility of making very large industrial tools.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics