Section _ reproduction and production of nanowires
Examining the degree of order and dimensions of nanowires produced using templates
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
_7xzq.gif)
Note: One-dimensional structures such as nanotubes, nanowires, and quantum wires are noteworthy structures in the fields of nanospintronics, nanophotonics, nanoelectronics, etc.
The reason for this attention is their large length-to-diameter ratio and the difference in their electrical, optical, chemical, and magnetic properties, which has led to their use as building blocks in nanoscale electronic and optoelectronic devices. Different methods for obtaining one-dimensional nanoarrays have been mentioned, among them are methods based on lithography (electron beam lithography, optical lithography, electric lithography, ion beam lithography, lithography by scanning microscopes), vapor phase deposition method. (Physical vapor deposition and chemical vapor deposition) and methods based on the use of templates. The electron in the atom, in addition to rotating around it under the influence of the gravitational force of the nucleus, also has a rotational movement around itself. This type of rotation in the structure of nanowires is called electron nanospin.
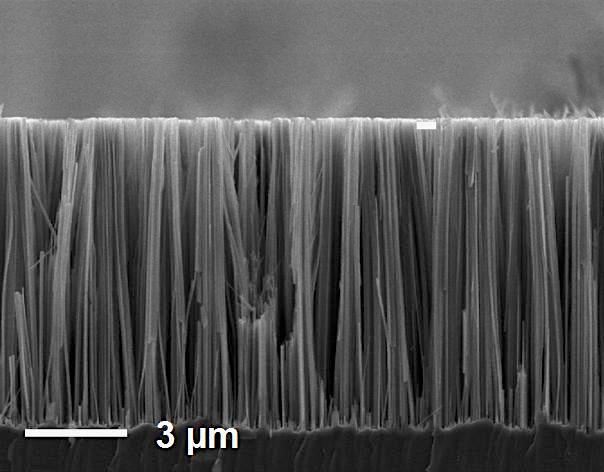
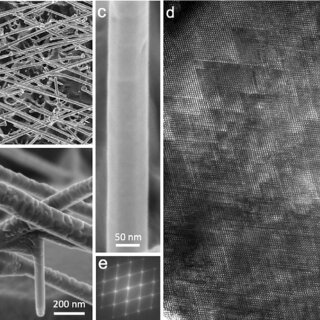
The advantages of using nanoporous aluminum oxide as a template for the production of nanowires compared to other methods include high porosity order, porosity alignment, controllable length-to-diameter ratio, and high porosity density. The order and dimensions of the nanowires produced using this set of templates are determined and controlled by the initial conditions of the anodizing process. Due to their chemical stability, high saturation magnetization, high axial anisotropy, high blinding temperature, excellent chemical stability and corrosion resistance, and high specific nanoelectrical resistance, they have good electromagnetic and nanomagneto-optical properties.
Conclusion:
One-dimensional structures such as nanotubes, nanowires, and quantum wires are noteworthy structures in the fields of nanospintronics, nanophotonics, nanoelectronics, etc.