Properties of metallic nanoparticles (optical properties; electrical properties; electromagnetic properties) based on nano-microelectronics (educational-research doctorate)
Researcher and author: PhD student Afshin Rashid
Note: These nanoparticles are widely used in various fields such as optical, electrochemical, electronic and catalytic applications. To improve their properties, they combine metal nanoparticles with other materials, one of the most important of which is graphene and its derivatives.
When nanoparticles form composites with graphene or graphene derivatives, they exhibit extraordinary catalytic activity. The surface of metal nanoparticles are considered catalytic sites. Particle size control has a significant effect on the properties of nanoparticles. The smaller the nanoparticle size, the higher the active level of the catalyst and the better the catalyst's performance.
Electrical properties of metal nanoparticles
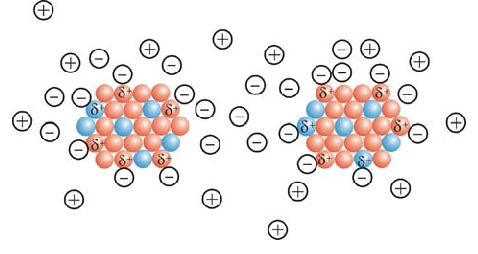
One of the most important properties of metal nanoparticles is electronic properties. Metal nanoparticles are a semiconductor with zero band gap and high electrical conductivity . As we know, each carbon atom has 1 electron that participates in chemical bonds, but in graphene each carbon atom is connected to nine other carbon atoms in a two-dimensional space. The remaining mononuclear atoms form a foot orbital at the top and bottom of the graphene plate, and these orbitals form double carbon-carbon bonds. Electronic properties are imposed on graphene by (orbital grafting ) and ( anti-grafting) double bonding. Graphene shows very high electron mobility at ambient temperature.
Optical properties of metal nanoparticles
The optical strength of metal nanoparticles 22 is the resistance to break m N 12 and its yang coefficient is Tpa 4. Despite its high hardness and strength, it is very light and has a density (1.77 ml / mg). The (optical) properties of the single-layer membrane of metal nanoparticles are measured using the AFM technique.
Electromagnetic properties of metal nanoparticles
Electromagnetic nanoparticles are particles that are less than one hundred nanometers in the presence of an external magnetic field that have nanomagnetic properties. The simplest structure of nanoparticles, including a magnetic nucleus (such as iron oxide, nickel and cobalt), and various non-magnetic coatings, are chemical compounds that are considered for some biological applications . For these applications, the particles must be characterized by high electromagnetic saturation and biocompatibility, and at the same time be capable of various functions. The surface of these particles has been modified with a number of organic fragments or non-metallic metals (such as gold) or oxide surfaces (such as silica and alumina) to provide a functional connection to a variety of biologically active molecules. Magnetic nanoparticles It can play an important role as a carrier of electromagnetic energy.