(nuclear power)
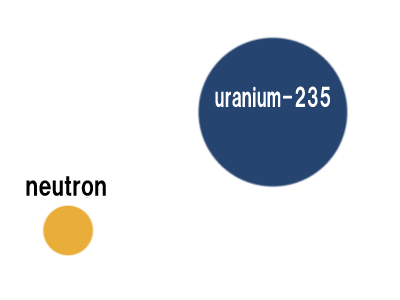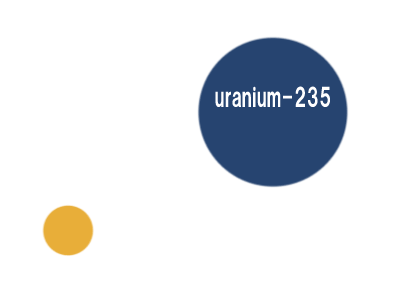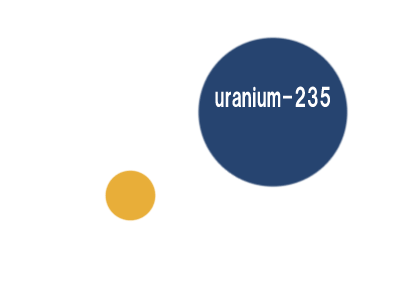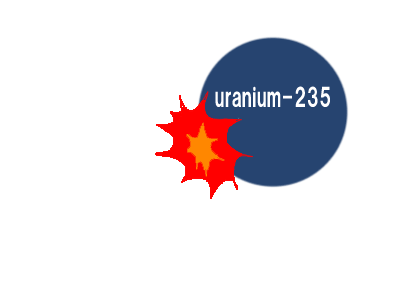
Nuclear electricity - an unlimited source of electrical energy "highly enriched uranium 235" in which 235U is more than 20% and in some cases even more than 98%
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Note: For the production of nuclear power, "low-enriched uranium" whose amount of 235U is less than 20% but more than 0.7%. Most nuclear power plant fuel is between 3 and 5% 235U, "highly enriched uranium" where 235U is more than 20% and in some cases even more than 98%.
Radioactive isotopes are also called unstable isotopes. In this type of isotope, the nucleus decays in the form of alpha, beta, electron capture, etc. and reaches more stable states of energy. Although these types of isotopes are dangerous, they have useful uses in life.
To produce an unlimited source of electrical energy (nuclear electricity) in the mined ore, uranium is separated from other elements during mechanical and chemical processes; In this way, the uranium ore is first crushed and milled in special machines, then it is purified during a chemical process including dissolving in acid and becomes a solid state, which is called yellow cake (U3O8). Yellow cake contains 70% of uranium and has radioactive properties. The yellow cake is solid, but in the next stage (enrichment) a special technology is used that requires a gaseous state. Therefore, to convert solid uranium oxide concentrate (U3O8) to uranium hexafluoride gas (UF6), the following steps are taken:
1__ First, the quality control of the concentrate particle size and fluidity is done on the yellow cake. Then, in order to produce UO2 powder from yellow cake (U3O8), dissolution, extraction, precipitation of UC9 and reduction are performed, and to convert UO2 to UF6 (green salt), it is combined with fluoric acid (HF) to obtain UF4. UF4 is then fluorinated with fluorine gas (9F) to finally obtain uranium hexafluoride (UF6), which is fed to a gas centrifuge where it is enriched.
2__ First, the quality control of the concentrate particle size and fluidity is done on the yellow cake. Then, in order to produce UO2 powder from yellow cake (U3O8), dissolution, extraction, precipitation of UC9 and reduction are performed, and to convert UO2 to UF6 (green salt), it is combined with fluoric acid (HF) to obtain UF4. Then UF4 is fluorinated with fluorine gas (9F) to finally obtain uranium hexafluoride (UF6), which is the feed of the gas centrifuge where it is enriched.
Conclusion :
For the production of nuclear electricity "low-enriched uranium" whose amount of 235U is less than 20% but more than 0.7%. Most nuclear power plant fuel is between 3 and 5% 235U, "highly enriched uranium" where 235U is more than 20% and in some cases even more than 98%.
Researcher and author: Dr. ( Afshin Rashid)
Specialized doctorate in nano-microelectronics